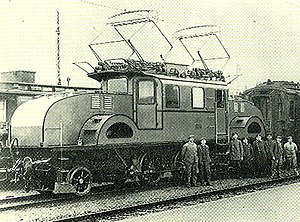
Baden A1
| A Badische 1 | |
|---|---|
|
A 1
|
|
| Numbering: | 1 |
| Number: | 1 |
| Manufacturer: | SSW , Maffei |
| Year of construction (s): | 1910 |
| Retirement: | 1923 |
| Axis formula : | 1'C1 ' |
| Gauge : | 1435 mm ( standard gauge ) |
| Length over buffers: | 13,160 mm |
| Fixed wheelbase: | 3500 mm |
| Total wheelbase: | 9500 mm |
| Service mass: | 66.0 t |
| Friction mass: | 42.0 t |
| Hourly output : | 770 kW at 42 km / h |
| Continuous output : | 440 kW at 42 km / h |
| Starting tractive effort: | 102.97 kN |
| Driving wheel diameter: | 1200 mm |
| Impeller diameter: | 850 mm |
| Power system : | 15 kV 16 2/3 Hz; |
| Power transmission: | Overhead line |
| Number of traction motors: | 2 AC series motors |
| Drive: | Parallel crank drive |
| Type of speed switch: | Rotary transformer without power interruption |
In the species A 1 the associated Badische state railway electric locomotive to operate on the Wiesentalbahn and wehra valley railway a.
history
Since the construction of the Wyhlen-Augst hydropower plant , the Baden railway has had the option of introducing electric train transport on its routes since the turn of the 20th century. The Wiesentalbahn and Wehratalbahn were chosen as the first route for electrification.
The energy from Wyhlen was conducted with two independently routed power lines to the Badischer Bahnhof, 10 km away, where complex forming technology had been installed. Right from the start, a rotating converter was used, which converted the input current from 10,000 V, 3 phases 50 Hz to 2 phases 15,000 V and 16 2/3 Hz by electromechanical means, the standard still used today. In addition, battery-based emergency power supplies and steam turbine generators were installed, but these were later shut down and expanded after the electricity network with DB + SBB networks made this superfluous.
The locomotive was chosen from several submitted designs, one developed by Siemens-Schuckert and Maffei . The locomotives should be able to move a 180 t train at 60 km / h on a 10 ‰ gradient. The maximum speed was 75 km / h.
Since the electrification of the line had not yet been completed when the locomotive was delivered in 1910, tests were carried out on the Murnau – Oberammergau line run by the local railway company . In the following year the machine pulled the inaugural train on the Bitterfeld – Dessau line and was shown at the industrial and commercial exhibition in Turin . From 1912 it was then used on the Baden routes. The locomotive had some technical defects. So she was prone to shaking vibrations. Attempts were made to reduce this with the locomotives of the following class A 2 . Because of these problems, she was only used for temporary work. In 1923 it came to the Altona port railway , but was dismantled that same year.
Constructive features
The locomotive had a frame made of cheeks stiffened with cross connections. The floor panels and traction motor mountings provided additional stiffening. The locomotive body was made of sheet steel. The engine room between the driver's cabs was not partitioned off. There was a half-height, narrow porch above each of the drive motors.
The traction motors it was AC - series motors with auxiliary excitement. The running axles did not have a reset device, so the locomotive was only guided by the coupling axles. The drive was carried out by a rod drive of two drive rods inclined at 45 ° on a jackshaft each.
Right from the start, both pantographs were pantographs , powered by compressed air, and had a bow knife. The oil transformer had an external cooling system with two fans. The primary winding could be switched to 5, 10 and 15 kV. It was controlled by a rotary transformer with an electric motor drive and four contactors .
The locomotive also had a compressed air brake, a sand spreader and a handbrake. The electrically operated train boiler was located in the engine room.
literature
- Hermann Lohr, Georg Thielmann: Baden Locomotive Archive (= Railway Vehicle Archive 2, 7) . transpress, Berlin 1988, ISBN 3-344-00210-4 .
- Dieter Bäzold, Günther Fiebig: German Locomotive Archive: Electric Locomotives . transpress, Berlin 1992, ISBN 3-344-70748-5 .
Web links
- Image of the locomotive on the Wiesentalbahn
- 1C1 Electric locomotive for the Wiesentalbahn (Baden) .. In: Die Lokomotive , year 1910, p. 198 ff. (Online at ANNO ).