Eightfold Way
As eightfold way (dt. The Eightfold Path , following the Eightfold Path of Buddhism wisdom) is a classification of hadrons in the framework of quantum chromodynamics called. Murray Gell-Mann and Yuval Ne'eman proposed it independently in 1961 in order to classify the newly discovered strange particles in the system of known particles. The eightfold way is considered to be the forerunner of the Quark model .
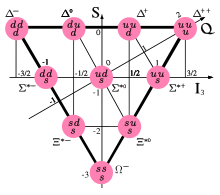
The is SU (2) - symmetry group of the isotopic spin to SU (3) - Flavor expanded, the under which mesons and baryons with spin are 1/2 respectively arranged as an octet (octet).
Baryons with spin 3/2 can be arranged in a decuplet, with the help of which the Ω - particle could be predicted even before it was experimentally discovered.
The eightfold way is explained today as a consequence of the flavor symmetries of the different types of quarks. Because the strong interaction has the same effect on all quarks regardless of the flavor, the mass of a hadron will remain roughly the same if you exchange one of its quarks. Mathematically, such an exchange is expressed by a group operation in SU (3) . The octets and decupplets are then representations of this group.
literature
Gell-Mann , Ne'eman : The Eightfold Way : With New Contributions from the Authors. Perseus Pub. 2000, ISBN 978-0738202990