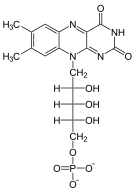
FAD synthetase
| FAD synthetase | ||
|---|---|---|
| Properties of human protein | ||
| Mass / length primary structure | 587 amino acids | |
| Cofactor | magnesium | |
| Isoforms | 5 | |
| Identifier | ||
| Gene name | FLAD1 | |
| External IDs | ||
| Enzyme classification | ||
| EC, category | 2.7.7.2 , nucleotidyl transferase | |
| Response type | Transfer of an adenylyl residue | |
| Substrate | FMN + ATP | |
| Products | FAD + PP i | |
| Occurrence | ||
| Homology family | FAD synthetase | |
| Parent taxon | Bilateria | |
FAD synthetase (also: FMN adenylyltransferase , gene : FLAD1 ) is the enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of flavin mononucleotide (FMN) in flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD) catalyzes . It is therefore indispensable for the utilization of riboflavin (vitamin B2), since it only functions as FAD in the metabolism. FAD synthetase is found in most animals ( Bilateria ). Five isoforms of the enzyme are known in humans .
Catalyzed reaction
An adenylyl residue is transferred from ATP to FMN and FAD and diphosphate are formed.
Individual evidence
Web links
Wikibooks: Biochemistry and Pathobiochemistry: Riboflavin Metabolism - Learning and Teaching Materials