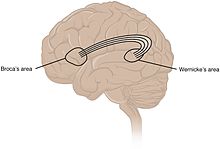
Arcuate fasciculus
The arcuate fasciculus ("curved bundle") is anatomically a pathway in the brain that connects within the human cerebral hemisphere with association fibers between areas of the cerebral cortex , the Wernicke area in the posterior temporal lobe and the Broca area in the lower frontal lobe .

The name Fasciculus arcuatus was coined by Karl Burdach in 1822 because of the arcuate course of the longer nerve fibers . Even if damage to this conduction pathway leads to characteristic speech disorders ( conduction aphasia ), according to recent studies, a more complex interconnection of the two brain areas is assumed.
In addition, neighboring brain structures such as the superior longitudinal fasciculus and fiber bundles of the extreme capsule are involved in the interconnections of a neural network that processes auditory signals in the sense of linguistic sounds and influences speech production. Comparative studies on the brains of living monkeys and humans using diffusion-weighted and functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) showed a pathway that was homologous to the human arcuate fasciculus, starting from the auditory cortex , in other primates as well. Common evolutionary forerunners of the human "language network" appear older than previously thought.
Individual evidence
- ↑ See HCP Tractographie Atlas on brain.labsolver.org.
- ↑ Heidi Johansen-Berg, Timothy EJ Behrens: Diffusion MRI: From quantitative measurement to in-vivo neuroanatomy. Academic Press, 2009, ISBN 9780080878515 , p. 404.
- ^ Karl Zilles, Bernhard Tillmann : Anatomie . Springer-Verlag, 2011, ISBN 9783540694830 , p. 757.
- ↑ F. Balezeau, B. Wilson, G. Gallardo et al .: primate auditory prototype in the evolution of the arcuate fasciculus. In: Nature Neuroscience. Volume 23, April 2020, pp. 611-614, doi: 10.1038 / s41593-020-0623-9 .
- ↑ Voice network in the human brain older than expected. Ärzteblatt.de, May 20, 2020; accessed on June 22, 2020.