Articulated locomotive
In the case of steam locomotives , an articulated locomotive is a locomotive with one or two steam bogies . In the case of electric locomotives (or diesel locomotives ), the term refers to a vehicle with a multi-part car body that is connected to one another by one or more joints .
Steam locomotives
Articulated locomotives were often used on narrow-gauge , field, and forest railroads because they were easy to turn . Their uneven running at higher speeds played a subordinate role there. In the United States, the "Big Boy", one of the largest steam locomotives ever built, was built as articulated locomotives. The disadvantage of the articulated locomotives was the difficult sealing of the moving steam pipes.
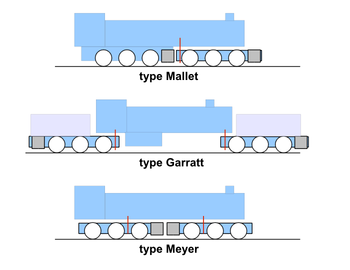
Well-known constructions are the types Mallet , Garratt , Meyer , Fairlie and Single Fairlie . Also Supports Ender locomotives and transmission locomotives are counted as articulated locomotives.
Electric locomotives
A similar concept as with the Garratt steam locomotives was used for the so-called crocodile locomotives . A bridge with the driver's cabs is placed in the middle on two movable motor bogies . A similar locomotive was being developed at the same time in the US with the Milwaukee Road EP-2 .
In another design, the two car bodies rest on a Jakobs bogie in between . It was used for the New Zealand EW class and in Italy for the E.636 , E.646 and E.656 . The RhB Ge 6/6 II in Switzerland differs from this design because its box joint between the two locomotive parts only allows vertical movements.
Not to be confused with the articulated locomotives are double locomotives , which consist of two structurally separate semi-locomotives.
See also
Notes and individual references
- ↑ Žarko Filipović: Electric railways: basics, locomotives, power supply; 2005, Springer-Verlag GmbH. ISBN 3-540-21310-4 , page 192
- ^ Hans-Peter Bärtschi: Electric locomotives from Swiss factories. In: Verkehrshaus der Schweiz (Ed.): Coal, electricity and rails: The railroad conquers Switzerland. Verlag NZZ, Zurich 1998, ISBN 3-85823-715-9 , page 256
- ↑ English Wikipedia page NZR EW class
- ^ A. Bächtiger: New B 0 B 0 B 0 narrow gauge locomotives of the Rh.B. with an output of 2400 hp. Schweizerische Bauzeitung, Volume 76 (1958), Issue 33, Page 484 (E-Periodica)
literature
- Erhard Born, Alfred Herold, Walter Trüb, (Ed.): Hobby Lexicon Railway. Rowohlt Taschenbuch, Reinbek near Hamburg, 1980, ISBN 3-499-16262-8 .
- Railroad Lexicon. Transpress VEB Verlag for Transport, Berlin, 1978.