Gogland
| Gogland | ||
|---|---|---|
| Map of Goglands | ||
| Waters | Gulf of Finland | |
| Geographical location | 60 ° 3 ′ N , 26 ° 59 ′ E | |
|
|
||
| length | 10.9 km | |
| width | 3 km | |
| surface | 21 km² | |
| Highest elevation | Lounatkorkia 176 m |
|
| Residents | approx. 50 2.4 inhabitants / km² |
|
| main place | Surkjulja (Суркюля) | |
Gogland ( Russian Гогланд , German mostly Hogland , also highlands , Finnish Suursaari , Estonian Suursaar , Swedish Hogland ) is an island in the Baltic Sea belonging to Russia .
location
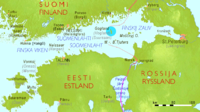
It is located in the Gulf of Finland roughly halfway between Estonia and Finland . The nearest town in Finland is Kotka, 40 km to the north . The closest Russian mainland is about 65 km southeast. Gogland belongs to the Kingisepp district of Leningrad Oblast . The island is known for its rocky landscape as well as its five lakes. Gogland is 12 km long and 1.5 to 4 km wide. The highest point in Gogland rises 176 meters above the Baltic Sea.
history
Gogland was settled by Finns at least since the 16th century and belonged to the Swedish sphere of influence resp. to the Finnish territories of the Kingdom of Sweden. During the Great Northern War , a sea battle took place near the island on July 22, 1713. Also in the Russo-Swedish War 1788–1790 , Russian and Swedish naval units fought near the island in 1788 in the Battle of Hogland . In the wake of a renewed Russian-Swedish war of 1808/09, Gogland fell to the Russian Empire in 1809, together with the new Grand Duchy of Finland , which was now so named . Finland gained independence from Russia in 1917 and gained state sovereignty after the Finnish Civil War in 1918. The majority of the islanders lived in two fishing villages that were administered from Viipuri (Vyborg).
Since 1826 there have been two measuring points of the Struve Arch on the Mäkiinpäällys hill , an elongated network of geodetic survey points built between 1793 and 1864.
Several shipwrecks lie in front of the island , for example, since October 1856, a three-masted clipper named "Amerika". The crew was buried in an old Finnish cemetery.
The island's first lighthouse was built in 1807, the tower that is now the longest in service dates from 1904.
The world's first radio transmission was made on Gogland in 1900 by Alexander Popow .
During the Soviet intervention of 1939–1940, known as the Winter War , Finnish residents were evacuated and the island fell and remained in Soviet hands. At the end of the Continuation War , German troops tried on September 15, 1944 in Operation Tanne Ost to occupy the island. Finnish troops prevented the German invasion , already under the terms of the Moscow armistice , while half of the German troops were captured. According to the armistice, the island had to be handed over to the Soviet Union soon afterwards.
After 1945 the log cabin settlement Suurkylä (Russian Суркюля, Surkjulja ) was razed and replaced by some modern buildings, some of which were used for a fishing kolkhoz , some for military purposes. Currently about 50 residents live permanently on the island, with fishing only being a leisure activity.
tourism
Gogland is increasingly visited by tourists from Saint Petersburg , but also by a few Finns. In 2006, Russian authorities declared the island of Gogland a border area, which means that foreigners can only enter the island with a special permit and at the same time only a small group is allowed to visit the island after considerable bureaucratic effort. This status is to be canceled again.
Measuring point of the Struve arch
Gogland (in the background) as seen from Kotka in Finland.