Granulocyte
Granulocytes ( singular : the granulocyte ; of Latin granule "granules" and ancient Greek κύτος Cytos , German , hollow ' ), and polymorphonuclear leukocytes (of ancient Greek πολύ poly , German , many' , ancient Greek μορφή morph , German , shape ' , ancient Greek λευκός leukós , German 'white' and ancient Greek κύτος cýtos , German 'cavity, vessel, shell' ) and formerly also called granulated leukocytes , are certain white blood cells. They make up 45 to 75% of all white blood cells ( leukocytes ).
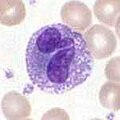
There are neutrophilic , basophilic and eosinophilic granulocytes , which are described and subdivided according to the staining behavior of the cytoplasm and which have different functions. Their main task is the unspecific fight ( innate immune response ) against bacteria , parasites and fungi . Some granulocytes are able to absorb and destroy pathogens. These granulocytes are therefore counted among the " phagocytes ".
Granulocytes are formed in the bone marrow and released into the blood . They can also leave the bloodstream and migrate into the tissue . The lifespan of basophils is about seven days, that of neutrophils one to four days. The granulocytes are broken down in the mononuclear phagocytosis system by monocytes .
The lower reference interval limit for adults is 2,000 / µl.
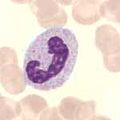
Neutrophil granulocyte , rod-shaped
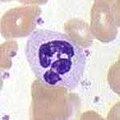
Neutrophil granulocyte , segmented
See also
Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ Basophile ( Memento of the original from January 27, 2013 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. , Reference database of the Charité.
- ↑ granulocytopenia. January 1, 2008, accessed on February 5, 2019 (German).