Haloacetic acids
The haloacetic acids are α- halo derivatives of acetic acid and a subgroup of the halocarboxylic acids . They are hydrophilic and corrosive . Compared to acetic acid, haloacetic acids are strong acids .
Since the haloacetic acids are strong enzyme inhibitors due to their reactions with sulfanyl (SH) groups , they can be used as preservatives . As little as 10 mg · l −1 have a preservative effect. Their use is prohibited today. In the past, bromoacetic acid was offered to prevent secondary fermentation in residual sweet wines.
Haloacetic acids are also formed when water is disinfected by chlorination , when hypochlorous acid reacts with organic carbon such as humic acids .
| Surname | Structural formula | pK s value |
|---|---|---|
| Chloroacetic acid |
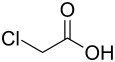
|
2.87 |
| Dichloroacetic acid (DCA) |

|
1.29 |
| Trichloroacetic acid (TCA) |

|
0.65 |
| Bromoacetic acid |

|
2.89 |
| Fluoroacetic acid |

|
2.59 |
| Trifluoroacetic acid (TFA) |
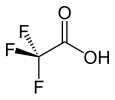
|
0.23 |
| Iodoacetic acid |

|
3.18 |
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b entry on haloacetic acids. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on October 12, 2014.
- ↑ Drinking water analysis . Disinfection by-products undesirable
- ↑ EPA: Basic Information about Disinfection Byproducts in Drinking Water: Total Trihalomethanes, Haloacetic Acids, Bromate, and Chlorite