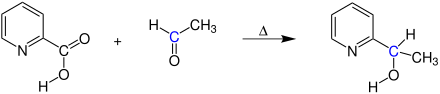Hammick reaction
The Hammick reaction is a name reaction in organic chemistry . The reaction was named after the English chemist Dalziel Hammick (1887–1966). During the reaction, an α-picolinic acid is reacted with a carbonyl compound to form a 2-pyridine alcohol.
Overview reaction
The Hammick reaction is carried out here using the reaction of picolinic acid with acetaldehyde as an example :
The reaction produces 1- (pyridin-2-yl) ethanol.
Reaction mechanism
The reaction mechanism of the Hammick reaction is explained here using the example given above:
In the picolinic acid ( 1 ), a hydrogen bond is formed between the nitrogen atom and the hydrogen atom of the alcohol group by heat . Carbon dioxide is then split off from picolinic acid 2 by electron rearrangement. It forms a pyridine - carbene 3 , which then attacks the carbonyl group of acetaldehyde and the alkoxide 5 arises. An intermolecular rearrangement of a proton forms the desired product 6 , 1- (pyridin-2-yl) -ethanol.
Individual evidence
- ↑ P. Dyson, DL Hammick: 362. Experiments on the mechanism of decarboxylation. Part I. Decomposition of quinaldinic and isoquinaldinic acids in the presence of compounds containing carbonyl groups . In: J. Chem. Soc. . 1937, p. 1724. doi : 10.1039 / jr9370001724 .
- ↑ DL Hammick, P. Dyson: 172. The mechanism of decarboxylation. Part II. The production of cyanide-like ions from α-picolinic, quinaldinic, and isoquinaldinic acids . In: J. Chem. Soc. . 1939, p. 809. doi : 10.1039 / jr9390000809 .
- ^ Z. Wang: Comprehensive Organic Name Reactions and Reagents, 3 Volume Set . John Wiley & Sons, Hoboken, New Jersey 2009, ISBN 978-0-471-70450-8 , p. 1314.