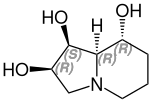Indolizidine alkaloids

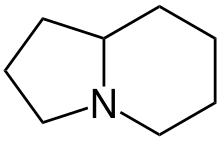
Indolizidine alkaloids are natural substances from various alkaloid groups, the structure of which can be derived from indolizidine .
Occurrence
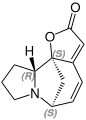
Indolizidine alkaloids occur in many plant families (including Elaeocarpaceae , Asclepiadaceae ) and as metabolites of fungi and bacteria. Slaframine and swainsonine were found, for example, in the fungus Rhizoctonia leguminicola and obtained by extraction. Castanospermine was obtained from the Australian chestnut . The alkaloids of this group also include pumiliotoxins , which are the toxins of the strawberry frog .
Representative
Polyhydroxy alkaloids
The polyhydroxy alkaloids include u. a. Castanospermine and swainsonine .
Pumiliotoxins
Main alkaloids of pumiliotoxins are pumiliotoxin A and pumiliotoxin B . Further representatives are Gephyrotoxin 223 AB and Gephyrotoxin
Phenanthroindolizidine alkaloids
Representatives of this alkaloid group are, for example, tylophorin and tylocrebrin and tylophorinidin .
Elaeocarpus alkaloids
Representatives of this group include a. Elaeokanin A , Elaeocarpin and Elaeocarpidin .
Securinega alkaloids
Securinin is the main alkaloid. Others are Securinol A and Norsecurinin .
Tylophora alkaloids
Most representatives of the Tylophora alkaloids are phenanthroindolizidine alkaloids such as B. Tylophorin, septicin and hispidine .
Ipomoea alkaloids
The main alkaloids in this group are Ipalbin and Ipomin . Also suitable Ipalbidin and Ipohardin ago.
properties
Swainsonine-type compounds are being studied as an anti- AIDS agent . Swainsonine and castanospermine act as inhibitors of sugar-breaking enzymes. Castanospermine also works against cancer cells and HIV viruses. Slaframine acts as a parasympathomimetic . Pumiliotoxin A increases the contraction of the striated muscles. Gephyrotoxin has a similar effect to pumiliotoxin A. Because of their diverse effects on the nervous system, these alkaloids are particularly popular. Their natural availability through extraction of frog skins is severely limited by species protection.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b Entry on indolizidine alkaloids. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on April 24, 2020.
- ↑ a b c d e H. Latscha, U. Kazmaier: Chemistry for biologists . 4th edition. Springer Spectrum, Berlin Heidelberg 2016, ISBN 978-3-662-47783-0 , p. 685 f .
- ↑ a b c G. Habermehl, P. Hammann, H. Krebs: Naturstoffchemie . 2nd Edition. Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg 2002, ISBN 978-3-540-43952-3 , p. 201 ff .
- ↑ E. Breitmaier: Alkaloids . Springer Fachmedien, Wiesbaden 1997, ISBN 978-3-519-03542-8 , pp. 44 f .
- ↑ Entry on phenanthroindolizidine alkaloids. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on April 25, 2020.
- ↑ Entry on Elaeocarpus alkaloids. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on April 25, 2020.
- ↑ Entry on Securinega alkaloids. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on April 25, 2020.
- ↑ Entry on Tylophora alkaloids. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on April 25, 2020.
- ^ Entry on Ipomoea alkaloids. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on April 25, 2020.