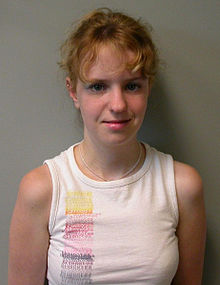Jacobsen Syndrome
| Classification according to ICD-10 | |
|---|---|
| Q93.5 | Other deletions of a part of a chromosome |
| ICD-10 online (WHO version 2019) | |
The Jacobsen syndrome is a chromosomal aberration (= chromosomal abnormality), in which in the q arm of chromosome 11 a deletion occurred. This deletion is mostly terminal, that is, it encompasses the telomere . However, the size of the deletion is not always the same, but varies among those affected. The syndrome is extremely rare and was first described by the Danish doctor Petra Jacobsen.
Symptoms
The symptoms of Jacobsen syndrome are very different and variable in severity. A characteristic phenotype is nevertheless recognizable.
Characteristic phenotype
- Trigonocephaly (triangular head)
- Hypertelorism (eyes set wide apart)
- Decreased growth
- Developmental delays
- Non-horizontal eyelid fold
- Strabismus (squint)
- Epicanthus medialis (Mongolian fold )
- Falling lower lip
- Mandibular Retrognathia (Retracted Jaw)
- Pronounced philtrum
- Split palate
- Short neck
- Deep and dysplastic ears
- Widely spaced nipples
- Hand furrows
Not only has the appearance of the affected persons changed, but they also often suffer from organ malformations and functional disorders.
organs
The most common symptom of the disease occurs in 94% of those affected. It is Paris-Trousseau syndrome , a congenital decrease in platelet production , which leads to increased bleeding .
56% of those affected suffer from a congenital malformation of the heart. In 2/3 of the cases this is the absence or hypoplasia of the left ventricle.
Neuronal and cognitive
Most children suffer from mild (IQ <80) to moderate (IQ <50) mental retardation (disability). Normal mental development is seldom encountered.
The patients have a normal perception, but have slight to moderate disorders in their expressiveness, i.e. their ability to express themselves. A disorder of fine and gross motor skills is also common.
Optical system
11% of those affected suffer from iris coloboma . This is a defect in the iris caused by a poor eye cup closure. In addition, a cataract (cataract) and a dysplastic retina often occur.
Molecular Aspects
The deletion in the q arm of the 11th chromosome is caused by a break within the chromosome. The most common break point is 11q23.3, also known as FRA11B . At this point on the chromosome there are a number of repeats of the nucleotide triplet “CCG”, which are also known as CCG repeats .
In Jacobsen syndrome, the CCG repeats expand and hypermethylate . As a result, the fragile site , which is sensitive to folic acid, is expressed in FRA11B, which presumably leads to rupture.
Another 6 break points have been discovered below the FRA11B. All contain CCG repeats , but no other fragile sites that are sensitive to folic acid . These deletions are inherited exclusively from the father. This indicates paternal imprinting . However, why this is the case and why a break in the chromosome can occur here is unclear.
forecast
About a fifth of affected children die within the first two years of life. The most common cause of death is a congenital heart defect, and occasionally bleeding. However, heart surgery, speech therapy, platelet transfusions, and regular check-ups can easily improve life expectancy and quality of life. No information has yet been published on the life expectancy of patients who survived the first two years.