Lattice filter
A lattice filter is a type of electronic filter that has a lattice structure. In the German-language literature, the term ladder structure is used as an alternative . The filter structure goes back to work from the 1920s by Otto Julius Zobel and George Ashley Campbell .
General
In terms of circuitry, this filter structure is used as an analog filter and in the context of digital signal processing as a digital filter and has the advantage that it can be easily checked for stability: If all coefficients are less than 1, the overall system is stable. As a digital filter, the structure can either be implemented as a filter with a finite impulse response (FIR) or as a filter with an infinite impulse response (IIR).
The characteristic impedance Z 0 of an analog basic element consisting of the individual complex impedances Z , as shown in the adjacent figure, is given as:
with the transfer function H (ω):
Digital realization
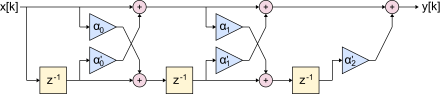
The following picture shows a 3rd order lattice filter in FIR structure as a digital filter. The sequence x [k] fed in from the left is converted into the output sequence y [k]. The values α 0 , α ' 0 ,… represent the filter coefficients per stage. The blocks labeled z −1 are delay elements by one sampling period:
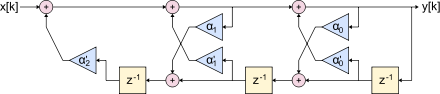
The next picture is a lattice filter in the form of an IIR structure. This structure is also known as the English all pole structure , since the transfer function only has poles and no zeros. The feedback is implemented in the lower line.
Applications
These filters are used primarily in the field of speech coding and speech synthesis . For example, cell phones that work according to the GSM standard use lattice filters in the IIR structure.
Extensive software packages are available for calculating the filter coefficients, such as the MATLAB program package with its latcfilt.m and tf2latc.m functions .
literature
- Alan V. Oppenheim: Time Discrete Signal Processing. Oldenbourg Verlag, 1999, ISBN 3-486-24145-1
Individual evidence
- ^ Otto Julius Zobel: Phase-shifting network , US patent 1 792 523, March 12, 1927, issued February 17, 1931.
- ↑ Otto Julius Zobel: Distortion Compensator , US patent 1 701 552, June 26, 1924, issued February 12, 1929.
- ^ SA Darlington: A history of network synthesis and filter theory for circuits composed of resistors, inductors, and capacitors , IEEE Trans. Circuits and Systems, Issue 31, pages 3-13 , 1984.