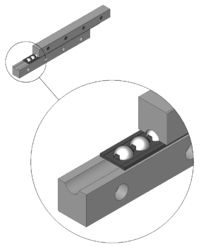
Rolling element cage
The roller retainer is next inner ring, outer ring and rolling bodies a component of rolling bearings . Rolling body cages in the form of open or closed chains are also used in various linear guides and ball screws . B. in profile rail guides, the terms ball chain or roller chain have naturalized as synonyms for the term roller cage.
In the case of cage rail guides , the term cage is used to characterize the type of guide, the terms ball cage, roller cage and needle cage usually also being used here.
The task of these cages is to keep the distance on the raceway, which is responsible for guiding the rolling elements. They ensure that the rolling elements do not touch one another or rub against one another in opposite directions and ensure that the load is distributed evenly through the even distribution of the rolling elements in the bearing . In the case of bearings or guides that can be dismantled, they also hold the rolling elements together and thus prevent them from falling out.
There are many materials that can be used in cages. For example, there are variants made of sheet metal , massive cages made of brass and increasingly plastic cages. These materials differ in their temperature properties, in their fat distribution behavior and in their suitability for different speeds or stroke frequencies .
In the case of bearing cages, a distinction is also made between cages guided by rolling elements, cages guided by the outer or inner ring.
To wear of rolling elements and raceways of bearings or guides to prevent unwanted by "walking" of the roller retainer, over were art history , various systems developed, the so-called cage creep reduce or (cage creeping) complete stop. (see also: stick-slip effect )