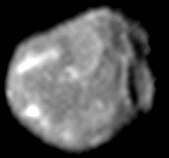
Lyctos Facula
Coordinates: 7 ° 0 ′ 0 ″ N , 172 ° 0 ′ 0 ″ E
The Lyctos Facula (also Mons Lyctos ) is a mountain up to 25 km high on the Jupiter moon Amalthea . A dark red color was made out on the surface of this satellite, which should be evidence of volcanic eruptions of Jupiter's moon Io . (The most prominent volcano on Io is Tupan-Patera .) Lactos Facula is a "twin" of Ida Facula.
Lyctos Facula is an elongated mountain with a length of 50 km. This mountain was discovered by Voyager 1 in 1979 and later photographed in greater detail by Galileo. Why the facula on Amalthea are brightly colored is not yet sufficiently clear. It is believed that a meteorite released this bright mass.
Naming
The mountain was named in 1979 by the IAU after the Cretan city of Lyktos .
See also
Web links
- Lyctos Facula in the Gazetteer of Planetary Nomenclature of the IAU (WGPSN) / USGS