MAP kinase pathway

|
The MAP kinase pathway ( MAP , English mitogen-activated protein ) describes in biology a number of multi-level signal transduction pathways that are involved in the regulation of embryogenesis , cell differentiation , cell growth and programmed cell death , among other things .
Signal path
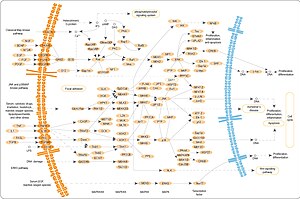
The MAP-kinase signaling pathways comprise at least three "series" connected kinases (see figure): A MAP-kinase-kinase-kinase (MAP-3K, also MAP-KKK), a MAP-kinase-kinase (MAP-2K, also MAP-KK) and a MAP kinase (MAP-K), which are activated (phosphorylated) in this order. One also speaks here of phosphorylation cascades .
A basic distinction is made between three different signal paths, which are activated by different factors. Activation via mitogens or growth factors at receptors activates the Raf → MEK 1/2 → ERK 1/2 cascade and is also called the ERK1 / ERK2 cascade, which can lead to cell growth , cell proliferation and differentiation . This signaling pathway is hyperactivated in 30% of all cancers . Activation via cytokines such as tumor necrosis factors or type 1 interleukin-1 receptor activates the MLKs / TAK / ASK1 → MKK 3/6 → p38 / MAPK-α / β cascade , which can result in responses such as inflammation , apoptosis, growth or differentiation . Activation via stress, UV light , heat shock or an osmotic shock activates the cascade MLKs / ASK-1 / MEKK-1/4 → MKK-4/7 → SAPK / JNK -1/2/3, which results in responses such as inflammation, Apoptosis , growth, or differentiation can result.
The activated proteins were named in the order MAP-3K → MAP-2K → MAP-K. The fact that more than one cascade of the form MAP-3K / MAP-2K / MAP-K can always be activated (which does not have to be restricted to one path in each case) complicates the MAP kinase path. For the sake of simplicity, only the most important enzymes have been mentioned here. The duration of the activation of a MAPK signal path depends, among other things, on the respective receptor. While activation of the EGF receptor leads to MAPK activation of around five minutes, MAPK activation takes several hours after activation of the NGFR . The phosphorylations are partially removed again by protein phosphatases such as PP2A or PP1C . MAP kinases can be inhibited by MAP kinase inhibitors .
Homologies


The triggers and the proteins involved in the MAP kinase pathway differ in part, depending on the environmental conditions of the cell. In unicellular organisms , the MAP kinase pathways are triggered by environmental factors such as lack of food, hyper- or hypotonic environments, but also pheromones . In mammalian cells, MAP kinase pathways are triggered by, among other things, ultraviolet light , oxidative stress , hypertonic environments, growth factors , cytokines, and differentiation factors .
MAPKK kinases
MAPKKK, e.g. B. Raf, activate the subsequent proteins in the signaling pathway by phosphorylation on serine or threonine side chains, which generally have a longer half-life than phosphorylated tyrosines.
MAPK kinases
The MAPKK, e.g. B. MEK, are also activated by phosphorylation in two places (either tyrosine or threonine), both phosphorylations are necessary to activate the kinase.
MAP kinases
The MAP kinases (MAP-K) themselves are small protein kinases with a molecular mass of 36,000-44,000 Da , which phosphorylate other proteins on specific serine , threonine or tyrosine residues. RAF and MAPK are serine / threonine-selective protein kinases. MEK (synonym MAPKK, kinase of MAP kinase) is a tyrosine / threonine kinase.
The MAP kinases are normally activated directly by phosphorylation at two sites. These are a tyrosine and a threonine , which are only separated by an amino acid . Both residues must be phosphorylated for the kinases to be active. The phosphorylation of these two amino acids is carried out by the MAP-KK, which is one step further "up" in the cascade (see figure). When the MAP kinases are activated, the transcription factors they phosphorylate are imported into the cell nucleus , thereby activating the transcription of a large number of target genes . As soon as the MAP kinases are dephosphorylated and thus inactivated, they are available for further activation cycles .
The MAP kinases (MAP-K) are divided into three groups. The extracellular signal-regulated kinases include the isoforms ERK -1, ERK-2 and ERK-5. There are also the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase and the c-Jun-N-terminal kinases ( JNK ).
literature
- G. Pearson, F. Robinson: Mitogen-Activated Protein (MAP) Kinase Pathways: Regulation and Physiological Functions. In: Endocr. Rev. Volume 22, 2001, pp. 153-183. PMID 11294822
- R. Seger, E. Krebs: The MAPK signaling cascade. In: FASEB J . Volume 9, 1995, pp. 726-735. PMID 7601337
Web links
- MAP Kinase Resource .
- KEGG : MAP Kinase Pathway
- Nomenclature of the mitogen-activated protein kinases
- MAPK cascade
Individual evidence
- ↑ L. Santarpia, SM Lippman, AK El-Naggar: Targeting the MAPK-RAS-RAF signaling pathway in cancer therapy. In: Expert opinion on therapeutic targets. Volume 16, number 1, January 2012, ISSN 1744-7631 , pp. 103-119, doi: 10.1517 / 14728222.2011.645805 . PMID 22239440 . PMC 3457779 (free full text).
- ↑ a b c d e Bruce Alberts: Ras Activates a Downstream Serine / Threonine Phosphorylation Cascade That Includes a MAP Kinase . In: Molecular Biology of the Cell. 4th edition. Garland 2002, ISBN 0-8153-3218-1 .
- ↑ MJ Garnett, R. Marais: Guilty as charged: B-RAF is a human oncogene. In: Cancer Cell . Volume 6, 2004, pp. 313-319. PMID 15488754
- ↑ JM Kyriakis, J. Avruch: Mammalian MAPK signal transduction pathways activated by stress and inflammation: a 10-year update. In: Physiological reviews. Volume 92, number 2, April 2012, ISSN 1522-1210 , pp. 689-737, doi: 10.1152 / physrev.00028.2011 . PMID 22535895 .
- ↑ B. Cseh, E. Doma, M. Baccarini: "RAF" neighborhood: protein-protein interaction in the Raf / Mek / Erk pathway. In: FEBS letters. Volume 588, number 15, August 2014, ISSN 1873-3468 , pp. 2398-2406, doi: 10.1016 / j.febslet.2014.06.025 . PMID 24937142 . PMC 4099524 (free full text).
- ↑ M. Cargnello, PP Roux: Activation and function of the MAPKs and their substrates, the MAPK-activated protein kinases. In: Microbiology and molecular biology reviews: MMBR. Volume 75, Number 1, March 2011, ISSN 1098-5557 , pp. 50-83, doi: 10.1128 / MMBR.00031-10 . PMID 21372320 . PMC 3063353 (free full text).