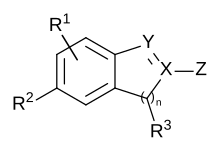
Markush formula
As a Markush structure , generic structure or General formula is referred to structural formulas with varying substituents , which are used especially in chemical patents. In tables, variable fragments in defined partial structures are indicated by abbreviations (R, R 1 ), which are defined in tables, e.g. B .:
- R, R ′, R 1 = alkyl radical
- X = heteroatom residue
- Ar = aryl radical
- E = ester group
- L = ligand

Connecting lines with a blind ending: polychlorinated dibenzodioxins
For variable numbers of groups, chain or ring links, italic subscripts are used, e.g. B. Cl x F 3 − x C − CCl y F 3 − y , H 3 C− [CH 2 ] m − 1 - [O − CH 2 −CH 2 -] n OH. Variable positions are indicated by a connecting line ending blindly between two positions and starting from the remainder.
It is named after Eugene A. Markush, who patented his invention.
Individual evidence
- ↑ Entry on Markush formulas. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on May 16, 2014.
- ↑ a b Patent US1506316 : Pyrazolone dye and process of making the same. Applied on January 9, 1923 , published August 26, 1924 , Applicant: Pharma Chemical Corp. Inventor: Eugene A. Markush.