Aryl group
An aryl group (abbreviated: Ar ) is an organic-chemical radical with an aromatic backbone. Aryl is thus the general name for a monovalent group of atoms which are derived from aromatic hydrocarbons by removing a hydrogen atom attached to the ring. Most aryl radicals are derived from benzene (C 6 H 6 ), the simplest aryl group is the phenyl group (Ph), (–C 6 H 5 ). Aryl residues can occur either as a fragment of a molecule (see table) or as an unstable free radical . Aryl cations are formed as reactive intermediates in the elimination of nitrogen from aryl diazonium salts , the so-called boiling of aryl-diazonium salts, aromatic alcohols to form (z. B. phenols ). Aryl anions also occur as reactive intermediates in organic syntheses and are more stable than aryl cations.
| Aryl residue | Surname | Structural formula | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Phenyl residue | toluene |  |
Phenyl residue: blue |
| Phenyl residue | phenol |  |
Phenyl residue: blue |
| Phenyl residue | Benzoic acid | 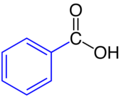 |
Phenyl residue: blue |
| 1-naphthyl radical | 1-naphthol |  |
1-naphthyl radical: blue |
| 2-naphthyl radical | 2-naphthylamine |  |
2-naphthyl radical: blue |
| 9-anthryl residue | 9-anthracene carbaldehyde |  |
9-anthryl residue: blue |
| 9-phenanthryl residue | Phenanthrene-9-boronic acid |  |
9-phenanthryl residue: blue |
The term aryl group is mainly used when one wants to formulate in general terms and does not want to specify which aromatic group is involved.
In contrast to aryl groups, the term alkyl groups is used to denote a radical that is not aromatic. There are also combinations of alkyl radicals and aryl radicals, one example is the benzyl radical [-CH 2 -C 6 H 5 ], which is derived from toluene by splitting off a hydrogen atom from the methyl group .
As biaryls (not: diaryls) refers to compounds in which two aryl groups are linked together via a single bond. The simplest biaryl is biphenyl .
See also
- Heteroaryl group or heteroaryl radical
- Aromatics
Individual evidence
- ↑ Entry on aryl groups . In: IUPAC Compendium of Chemical Terminology (the “Gold Book”) . doi : 10.1351 / goldbook.A00464 Version: 2.1.5.
- ^ Brockhaus ABC chemistry. VEB FA Brockhaus Verlag, Leipzig 1965, p. 112.
- ↑ Otto-Albrecht Neumüller (Ed.): Römpps Chemie-Lexikon. Volume 1: A-Cl. 8th revised and expanded edition. Franckh'sche Verlagshandlung, Stuttgart 1979, ISBN 3-440-04511-0 , p. 283.
- ↑ Jonathan Clayden, Nick Greeves, Stuart Warren, Peter Wothers: Organic Chemistry. Oxford University Press, Oxford 2001, ISBN 978-0-19-850346-0 , pp. 599-600.
- ↑ Jonathan Clayden, Nick Greeves, Stuart Warren, Peter Wothers: Organic Chemistry. Oxford University Press, Oxford 2001, ISBN 978-0-19-850346-0 , pp. 600-604.
- ^ Siegfried Hauptmann : Organic chemistry . 2nd Edition. VEB Deutscher Verlag für Grundstofftindustrie, Leipzig 1985, ISBN 3-342-00280-8 , p. 267.