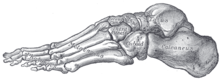
Metatarsal bones
The metatarsal bones - in Latin ossa metatarsalia (plural) or os metatarsale (singular) - are located in the foot between the tarsus and the toes.
Expression
In the case of the land vertebrates , the foot in the blueprint has five toes and thus also five metatarsal bones, which are also present in most recent vertebrates. In some groups, individual toe rays were reduced, fused together, or otherwise modified. In ungulates , for example, several toes are sometimes reduced and in many groups the metatarsals are fused to a different extent to form a cannon bone . In birds , the metatarsals are fused with the distal tarsal bones to form the tarsometatarsus .
Like all primates, humans have five metatarsal bones on each foot, which are numbered 1 to 5 from the inside (medial) to the outside (lateral). The metatarsal bone, which runs on the inner edge of the foot from the tarsus to the big toe, is called the first metatarsal bone. Together with the big toe, the first metatarsal bone forms the so-called first ray. Accordingly, all other metatarsal bones together with the adjoining toes form the second, third, fourth and fifth rays.
construction
The metatarsals have the following components:
- Base
- Body (corpus)
- Head (metatarsal head, caput)
In the area of the base of the first metatarsal there is an extension called the first metatarsal tuberosity . This extension serves as an attachment to the tibialis anterior muscle . In the area of the base of the fifth metatarsal bone there is also an extension called the V metatarsal tuberosity . This extension serves as a starting point for the peroneus brevis muscle .
Articular surfaces
The articular surfaces of the heads are convex and form the metatarsophalangeal joints with the proximal toe phalanx .
The articular surfaces of the bases are more or less flat. They are in contact with the tarsus and form the Lisfranc joint line ( Articulationes tarsometatarseae ). The bases of the first to third metatarsal bones each form a joint with the first to third sphenoid bones . The bases of the fourth and fifth metatarsals are connected to the cuboid bone . In addition, the metatarsal bones are in contact with one another through intermetatarsal joints . On the underside of the head of the first metatarsal there are small furrows in which the sesame bones of the big toe lie.
Supination, pronation
The metatarsal bones can be moved slightly fan-shaped against each other and thus enable a mobility in the forefoot area, which is referred to as supination and pronation . As a result, the forefoot is able to adapt to unevenness when walking.
Proportions
The first metatarsal is the shortest and strongest bone with the largest cross-section. The large cross-section is necessary because when walking, most of the unrolling occurs via the big toe and thus via the 1st ray. The second metatarsal is the longest metatarsal. The length of the following metatarsals decreases continuously towards the lateral edge of the foot.
Other common features
All metatarsal bones are tubular bones . The bases are designed wider towards the back of the foot than towards the sole of the foot. This results in an approximate wedge shape, which, like the cuneiform bones ( Ossa cuneiformia ), also forms the transverse arch of the foot.
Fractures and diseases
In diseases such as hallux valgus and splayfoot there are changes in the position of the metatarsals.
Direct blows to the forefoot can break the metatarsal bones. Also possible are so-called stress fractures , i.e. bone fractures that are not caused by a sudden application of force (accident or the like), but are due to fatigue of the bone material ( marching fracture ). The fracture of the fifth metatarsal bone at the proximal end of the diaphysis is known as the Jones fracture . If the cause has not yet been clarified, aseptic bone necrosis (bone infarction ) of one metatarsal head, usually the second, can occur ( Köhler-Freiberg's disease ).
A congenital shortening of a metatarsal bone is called brachymetatarsia , and the first and fourth metatarsals are most commonly affected.