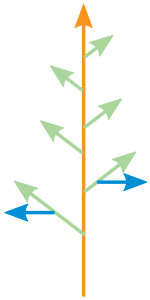
Monopodium
A Monopodial referred to in plants in the form of a branch with continuous shoot axis . The previous year's shoot section is continued annually by the same, akroton (at the top) promoted top meristem.
With a compound inflorescence , monopodial branching is called racemous . Partial inflorescences of the same type go from only one main axis. Further branches are possible, but only if all branches of the main axis have the same basic plan. Examples of a compound racemous inflorescence are grape , umbrella grape , ear , double ear , piston , head , basket , umbel and double umbel .
The counterpart to the monopodium is the sympodium , in which not the main shoot, but one or more side shoots continue to grow. These unsymmetrical branches lead to a zymous inflorescence.