Bulbospongiosus muscle
| Bulbospongiosus muscle |
|---|
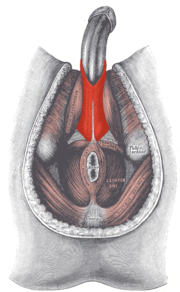 M. bulbospongiosus in men |
| origin |
| Male: • Centrum perineum • Raphe corporis bulbospongiosi Woman: |
| approach |
| Men: • Inferior urogenital diaphragm fascia of the penis Woman: |
| function |
| Men: • Compression of the erectile tissue of the urethra Woman: |
| Innervation |
| Pudendal nerve |
| Spinal segments |
| S2-S4 |
The bulbospongiosus muscle (also obsolete bulbocavernosus ) is a striated muscle in the area of the genital organs . In male mammals, it surrounds the initial section of the erectile tissue of the urethra ( Bulbus penis ). The equivalent in female mammals is the sphincter muscle of the vulva and the vaginal vestibule . It is therefore also subdivided into the constrictor vulvae and the vestibular constrictor muscle .
The bulbospongiosus muscle performs rhythmic contractions in both sexes during orgasm . In men, these generate a pulsating pressure wave in the erectile tissue of the urethra, which supports the ejaculation of the sperm . Corresponding pulsating contractions occur in women. The muscle can also be voluntarily contracted.
The muscle is severed as part of a perineal incision that becomes necessary during childbirth (only with mediolateral and lateral episiotomy ). As a rule, the cut heals relatively quickly afterwards.
Web links
- H. Jastrow: The human muscles in tables. University of Mainz
