Numbering (telecommunications)
Numbering (engl. Numbering ) is for addressing in telecommunications the assignment of sequences of digits to terminals or communication networks to these. A well-known example of numbering is the numbering plan for telephone numbers, but addressing on the Internet using IP addresses or postal delivery using postcodes are also carried out using sequences of digits.
Numbering in voice networks
Number assignment according to ITU-T E.164
Main article: E.164
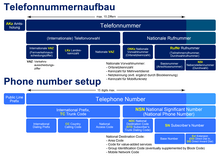
Numbers are assigned in voice networks on the basis of recommendation E.164 of the ITU-T . An international E.164 call number is therefore an address that is limited in length to 15 digits (without the traffic elimination number) and which is divided into different blocks. Common international numbers consist of
- a country code (e.g. 49 for Germany) with 1 to 3 digits, which determines the destination country of the call,
- a National Destination Code (NDC), which can dial, for example, a local area network (30 for Berlin), a network operator code or a value-added service (800 for toll-free connections), and
- the subscriber number (SN, Subscriber Number ), possibly with extension digits for a telephone system .
Traffic elimination rate
Main article: Traffic elimination rate
When establishing a telephone connection, national and international prefixes can be used to select the desired country, local network or the respective service. In order to be able to set up the telephone connection, however, the network needs the national or international traffic code as signaling information in addition to the actual area code. In most countries the VAZ for domestic connections is 0 (Hungary has the VAZ 06 ), while the VAZ for the international plane is mostly 00 .
Open and hidden numbering
Open numbering
If subscribers can establish a connection to one another within the same numbering range, for example in the same local network, simply by dialing the subscriber number, this is called open numbering . With open numbering, the initiator of a connection needs to know which numbering range he is in in order to be able to decide whether he has to use an area code or not. Based on this concept, it is possible in an open-numbered network to draw conclusions about the location of the subscriber from the complete call number or the area code. An example of open numbering is the addressing of subscribers within a telephone system.
Concealed numbering
With hidden numbering, the subscribers always have to dial the full number, regardless of whether both connections are in the same network or not. The code of the numbering range is an integral part of the phone number. Since the entire number including the numbering range is transferred with hidden numbering in the case of number portability , in contrast to open numbering, conclusions about the location or service provider are not possible or only possible to a limited extent. Concealed numbering is used, for example, in the German cellular network .
Universal Personal Telecommunications
Universal Personal Telecommunications (UPT), an ITU concept from 2001, extends the principle of hidden numbering to include the international level. With the country code 878 it is possible to get a worldwide uniform number.
See also: personal phone number
Numbering in data networks
Main article: IP address
Addressing in data networks usually also takes place via a numerical address, the so-called IP address. In the currently most widespread version of the IP protocol, IPv4 , an IP address consists of four bytes, i.e. four blocks with the numerical values 0 to 255. In the dotted decimal notation , these four decimal blocks are separated by dots, for example, an address is “192.168.0.27”. On the Internet , however, services are usually addressed by the user via alphanumeric domain names, as these are easier to remember. An IP address is assigned to this name, which can be resolved via the Domain Name System .
Since with IPv4 theoretically 2 32 , i.e. 4,294,967,296 possible addresses are available, but large parts of them cannot be used publicly due to the generous reservation of certain address areas, IPv6 has meanwhile been developed to avoid an address shortage. IPv6 allows an addressing space with a maximum of 2 128 addresses.
Telephone Number Mapping (ENUM)
Main article: Telephone Number Mapping
Since the development of IP telephony, there has also been a need to integrate the traffic of the voice and data networks. The Telephone Numbering Mapping - ENUM for short - was developed for this purpose. An E.164 number is translated into an IP address using ENUM. One or more destinations can then be specified for this address via the Domain Name System, which can have different priorities. When dialing an ENUM telephone number, the call can consequently be switched to different connections or services depending on the stored preference of the called party.
literature
- Gerd Siegmund: Technology of the networks, 4th edition. Hüthig Verlag, Heidelberg 1999.
- International Telecommunication Union: ITU-T Recommendation E.164: The international public telecommunication numbering plan, status 02/2005 . ( online )
Individual evidence
- ^ Government Decree No. 164/2005. (PDF) (No longer available online.) August 16, 2005, p. 9 , formerly in the original ; accessed on June 7, 2010 (English). ( Page no longer available , search in web archives ) Info: The link was automatically marked as defective. Please check the link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.