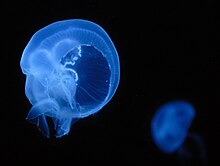
Ear jellyfish
| Ear jellyfish | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

Ear jellyfish ( Aurelia aurita ) |
||||||||||||
| Systematics | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| Scientific name | ||||||||||||
| Aurelia aurita | ||||||||||||
| Linnaeus , 1758 |
The ear jellyfish ( Aurelia aurita ) belongs to the class of umbrella jellyfish (Scyphozoa) within the cnidarians (Cnidaria). It is distributed almost worldwide in the oceans from around 70 ° north to around 55 ° south. It is also found on the German North Sea coast and in the western areas of the Baltic Sea , since the salinity of the water is still sufficient for its living needs. Reproduction takes place in the western Baltic Sea to the southern Bodden Sea . However, recent molecular genetic studies indicate that it is a complex of several cryptic species .
Appearance
The ear jellyfish has a flat arched umbrella, which is about 20-30 centimeters tall, with four ring-shaped sexual organs in the color brownish red and four curtain-like hanging, brownish mouth arms. The shade is white to yellowish.
Reproduction
The ear jellyfish begins to release eggs into open water after fertilization . The eggs go through early development, at the end of which the gastrula forms the so-called mobile planular larva . This mobile larva turns with the mouth opening upwards and attaches itself to the ground (sessile planular larva) and forms a polyp there, which multiplies through lateral budding or strobilation (constriction). The strobilation creates ephyral larvae that are only a few millimeters in size. These then grow into mature medusas.
Locomotion
Jellyfish swim through a contracting movement of their umbrella, in which they simultaneously expel water downwards according to the principle of recoil. They move diagonally upwards, only to let themselves fall down a little afterwards. They therefore often swim close to the surface of the water. With this principle, they can travel up to ten kilometers per hour. Often, however, they can simply be drifted with the current.
Special
In the not yet fully grown medusa, called Ephyra, a so-called rhopalium can be seen in the tentacles under the light microscope . This rhopalium consists of a lens to perceive light stimuli and a statolith , which moves when the jellyfish is displaced and thus tells the jellyfish what position it is in. The moon jellyfish consists of 98.2% water.
swell
Individual evidence
- ^ Report on moon jellyfish offspring. Archived from the original on March 31, 2016 ; accessed on December 17, 2019 .
- ↑ Rainer Flint: Biology in Numbers: A collection of data in tables with over 10,000 individual values. Spektrum Verlag 2002
literature
- Mike N. Dawson and Laura E. Martin: Geographic variation and ecological adaptation in Aurelia (Scyphozoa, Semaeostomeae): some implications from molecular phylogenetics. Hydrobiologia, 451: 259-273, Dordrecht 2001 ISSN 0018-8158 PDF
- Ernst Horstmann: Investigations on the physiology of the swimming movements of the Scyphomeduses Aurelia aurita and Cyanea capillata , in Pflüger's archive for the entire physiology of humans and animals . Volume 234, Issue 4, Würzburg 1934, DNB 570715172 (Dissertation University of Kiel 1934, 28 pages, with illustrations).