Pagoclone
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
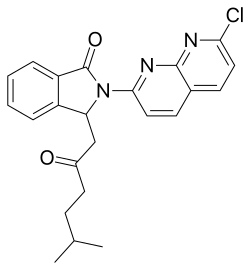
|
||||||||||||||||
| Simplified structural formula without stereochemistry | ||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Pagoclone | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
(+) - 2- (7-chloro-1,8-naphthyridin-2-yl) -3- (5-methyl-oxohexyl) -2,3-dihydro-1 H -isoindol-1-one |
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 23 H 22 ClN 3 O 2 | |||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 407.899 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Pagoclon is an anti- anxiety agent ( anxiolytic ) from the chemical group of cyclopyrrolones . It is structurally related to the drug zopiclone , which is used as a sleep aid.
Pharmacological profile
Pagoclon binds to the benzodiazepine binding site of human GABA A receptors , which contain either an α 1 , α 2 , α 3 or α 5 subunit. The binding affinity is 0.7–9.1 n mol · L −1 . Pagoclon acts as a partial agonist at α 1 -, α 2 - and α 5 -containing GABA A receptors, whereas it acts as a full agonist at receptors containing an α 3 subunit. In rats, 5'-hydroxypagoclone was identified as the main metabolite . This metabolite is much more effective in the α 1 subtype than the starting compound and shows significant anxiolytic activity and sedation . In contrast to zopiclone, pagoclone has an anxiolytic effect in low doses and only slightly sedating or amnesic. The British pharmacologist David Nutt considers pagoclon and similar substances ( bretazenil ) to be suitable for replacing drinking alcohol. It produces positive effects of alcohol such as relaxation and socializing, but without causing negative effects such as aggression, amnesia , nausea, and liver damage.
Pagoclon has an anti-anxiety effect when taken orally at 0.5–1 mg. With an oral dose of 1-2 mg pagoclon, there is also slight sedation. A hypnotic effect does not come about up to a dose of 10 mg. A benzodiazepine effect cannot be achieved with normal dosages. The plasma half-life is rather short at around 4 to 6 hours.
Experimental use
Pagoclon was tested as a possible drug against stuttering . In an eight-week controlled study with 132 participants, significant improvements in symptoms were found with few side effects. Similar positive results were seen in 119 people who chose to continue treatment during an open-label one-year renewal period. In later studies with a larger group of people, the results were not significant, which led to research being discontinued.
A study of 16 patients with panic disorder (agoraphobia or claustrophobia) was positive. 0.1 mg pagoclon given three times a day significantly reduced the frequency of panic attacks. There was no significant difference in the secondary endpoints .
There are no finished medicinal products on the market.
synthesis
Pagoclon can be obtained by a multi-stage reaction. First, the reaction of 2-amino-7-chloro-1,8-naphthyridine with phthalic anhydride leads to the corresponding phthalimide. The selective reduction of one of the imide carbonyl groups gives the corresponding alcohol. The reaction with the carbanion from ethyl 5-methyl-3-oxohexanoate leads to pagoclon by displacement of the hydroxyl group.
Individual evidence
- ↑ This substance has either not yet been classified with regard to its hazardousness or a reliable and citable source has not yet been found.
- ↑ Lingford-Hughes A., SJ Wilson, A. Feeney, PG Grasby, DJ Nutt: A proof-of-concept study using [ 11 C] flumazenil PET to demonstrate that pagoclone is a partial agonist . In: Psychopharmacology . 180, No. 4, 2005, pp. 1-3. doi : 10.1007 / s00213-005-0060-1 . PMID 15986186 .
- ↑ Atack JR, Pike A., Marshall G., Stanley J., Lincoln R., Cook SM, Lewis RT, Blackaby WP, Goodacre SC, McKernan RM, Dawson GR, Wafford KA, Reynolds DS: The in vivo properties of pagoclone in rat are most likely mediated by 5'-hydroxy pagoclone . In: Neuropharmacology . 50, No. 6, 2006, pp. 677-89. doi : 10.1016 / j.neuropharm.2005.11.014 . PMID 16430927 .
- ↑ JR Atack: The benzodiazepine binding site of GABA (A) receptors as a target for the development of novel anxiolytics . In: Expert Opinion on Investigational Drugs . 14, No. 5, May 2005, pp. 601-18. doi : 10.1517 / 13543784.14.5.601 . PMID 15926867 .
- ↑ JR Atack: Anxioselective compounds acting at the GABA (A) receptor benzodiazepine binding site . In: Current Drug Targets. CNS and Neurological Disorders . 2, No. 4, August 2003, pp. 213-32. doi : 10.2174 / 1568007033482841 . PMID 12871032 .
- ↑ DJ Nutt: Alcohol alternatives - a goal for psychopharmacology? In: J Psychopharmacol. tape 20 , no. 3 , May 2006, pp. 327-8 , doi : 10.1177 / 0269881106063042 .
- ↑ a b G. Maguire, D. Franklin, NG Vatakis, E. Morgenshtern, T. Denko, JS Yaruss, C. Spotts, L. Davis, A. Davis, P. Fox, P. Soni, M. Blomgren, A Silverman, G. Riley: Exploratory randomized clinical study of pagoclone in persistent developmental stuttering: the EXamining Pagoclon for peRsistent dEvelopmental Stuttering Study. . In: Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology . 30, No. 1, February 2010, pp. 48-56. doi : 10.1097 / jcp.0b013e3181caebbe . PMID 20075648 .
- ^ JJ Sandford et al .: Crossover trial of pagoclone and placebo in patients with DSM-IV panic disorder. In: J Psychopharmacol. tape 15 , no. 3 , September 2001, doi : 10.1177 / 026988110101500312 .
- ↑ Google Patents: US4960779A - Pyrrole derivatives, and pharmaceutical compositions which contain them and pharmacological methods of use - Google Patents , access date : July 10, 2019.
