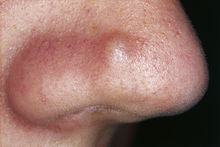
Papule
| Classification according to ICD-10 | |
|---|---|
| R23.8 | Other and unspecified skin changes |
| ICD-10 online (WHO version 2019) | |
As a papule (from latin papula , vesicle ') or nodules is referred to in the medicine is up to pea-sized raised thickening of the skin . It is one of the primary skin changes (primary efflorescences) and can recede completely without scarring . Focal confluent papules are called plaques . The formation of papules can be caused by various skin diseases . Triggers can be insect bites , bacterial infections, dermatophytoses , protozoa ( leishmaniasis ), parasites ( scabies , sarcoptic mange ), allergies or skin tumors .
According to localization in the layers of the skin, the following forms are distinguished:
- The epidermal papule is a proliferation of cells in the horny ( stratum corneum ) or prickly cell layer ( stratum spinosum ) of the epidermis . The epidermal papule can consist of normal skin cells (e.g. a wart ), tumor cells (epithelial lymphoma ) or inflammatory cells ( leukocytes ). Inflammatory papules are reddened and can develop into pustules .
- The cutaneous papule is a multiplication of cells of the dermis (corium) as it occurs, for example, in secondary syphilis or nevus cell nevus .
- The epidermo-cutaneous papule is the mixed form in which cells multiply in both the epidermis and the dermis. Epidermo-cutaneous papules occur, for example, in eczema or lichen planus .
See also
literature
- B. Savic (Editor): General Clinical Investigations . Springer, 2013, ISBN 978-3-662-00621-4 , pp. 11 .
Individual evidence
- ↑ Alphabetical directory for the ICD-10-WHO Version 2019, Volume 3. German Institute for Medical Documentation and Information (DIMDI), Cologne, 2019, p. 672