Phocomelia
| Classification according to ICD-10 | |
|---|---|
| Q73.1 | Phocomelia of unspecified limb (s) |
| ICD-10 online (WHO version 2019) | |
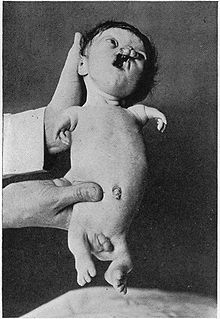
Phocomelia (from ancient Greek φώκη phōkē 'seal, seal' and μέλος mélos 'limb'; synonyms seal limb and phocomelus ) denotes a malformation of the limbs of the fetus ( dysmelia ) with fin-like seating of the hands or feet on the shoulder or hip joint or missing long ones Long bones of the limbs .
Phocomelia, like other types of dysmelia, can be inherited, for example in Roberts syndrome or Al-Awadi-Raas-Rothschild syndrome , or caused by external influences, for example as side effects of drugs and hormone preparations .
The best-known example of drug side effects that cause phocomelia is thalidomide , the active ingredient in Contergan , which was launched in the late 1950s. It was intended to be used as a sleep aid for women during pregnancy , among other things , but in thousands of cases it caused dysmelia, particularly phocomelia, in the growing fetus . This led to the drug being removed from the regulatory market in 1961 .
Dysmelia can be detected in the womb as part of prenatal diagnostics using fine ultrasound .
A special form of phocomelia is tetraphocomelia , in which all four extremities are shortened.
Individual evidence
- ^ Pschyrembel . Medical dictionary. 257th edition. Walter de Gruyter, Berlin 1993, ISBN 3-933203-04-X , p. 1186 .
- ^ Wilhelm Gemoll : Greek-German school and hand dictionary . G. Freytag Verlag / Hölder-Pichler-Tempsky, Munich / Vienna 1965.
- ↑ Medical Lexicon