Polygordius
| Polygordius | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||||
| Systematics | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| Scientific name of the order | ||||||||||||
| Polygordiida | ||||||||||||
| Pettibone , 1982 | ||||||||||||
| Scientific name of the family | ||||||||||||
| Polygordiidae | ||||||||||||
| Czerniavsky , 1881 | ||||||||||||
| Scientific name of the genus | ||||||||||||
| Polygordius | ||||||||||||
| Schneider , 1868 |
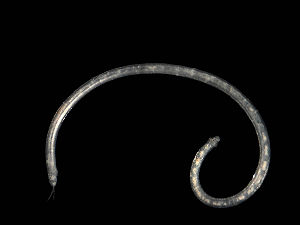
In the genus Polygordius , with around 15 species at the same time mono generic family Polygordiidae and the order Polygordiida forms, is a group of minute to less than, in the sand gap system of live and from bacteria Autotrophic polychaetes to find (Polychaeta) in seas worldwide are. Due to their weak or missing segmentation and often nonexistent parapods and bristles can easily with roundworms be confused.
features
The Polygordiidae have a slender, thread-like body, up to 10 cm long and 1 mm wide, which can count about 185 segments. On the prostomium there is a pair of firm, stiff palps (also known as " tentacles ") and, in some species, two pigmented eyes. An external segmentation is difficult to see or even completely absent, and the body surface is smooth and slightly iridescent. There is lashing in the nuchal slits, sometimes on the palps and rarely in scattered tufts of eyelashes. Parapodies are missing as well as bristles. There is a circle of glue glands on the bulbous pygidium, and a pair of anal cirrus may also be present.
habitat
The Polygordiidae live in the sand gap system of coarse sediments on sea shores and in the tidal zone .
Development cycle
The Polygordiidae are usually separate sexes, but Polygordius triestinus was described as a hermaphrodite . The egg cells and sperm are released into the open sea water by tearing the body wall, where fertilization takes place. The development initially proceeds via a freely swimming trochophora larva, which then either develops into an "exolarva", in which the newly formed segments hang at the back of the front part of the larva (as in Polygordius neapolitanus ) or into an "endolarva" in which the newly formed segments are turned inside out (as in Polygordius appendiculatus ). During the metamorphosis into a creeping worm, the animal throws off part of its body and eats it up.
Systematics
In 1868, Friedrich Anton Schneider described the type Polygordius lacteus at the same time as the genus Polygordius . In 1882 Voldemar Czerniavsky established the monogeneric family Polygordiidae. In 1904 John Percy Moore described the new species Chaetogordius canaliculatus from Cape Cod in a new monotypical genus , which, in contrast to the Polygordius species, has bristles on the rear segments. Since then, this species has not been found, and according to Rota and Carchini (1999), body parts of different species were the basis for this species description, which would make it invalid. The Polygordiidae are now regarded as a monogeneric family with the only genus Polygordius . Marian Hope Pettibone described the order Polygordiida in 1982 with the only family Polygordiidae.
The genus Polygordius includes the following species :
- Polygordius antarcticus Rota & Carchini, 1999
- Polygordius appendiculatus Fraipont, 1887
- Polygordius epitocus Dawydoff, 1905
- Polygordius erythrophthalmus (Giard, 1880)
- Polygordius eschaturus Marcus, 1948
- Polygordius ijimai Izuka, 1903
- Polygordius jouinae Ramey, Fiege & Leander, 2006
- Polygordius lacteus Schneider, 1868
- Polygordius leo Marcus, 1955
- Polygordius madrasensis Aiyar & Alikuhni, 1944
- Polygordius neapolitanus Fraipont, 1887
- Polygordius pacificus Uchida, 1935
- Polygordius triestinus Woltereck in Hempelmann, 1906
- Polygordius uroviridis Aiyar & Alikuhni, 1944
- Polygordius villoti Perrier, 1875
literature
- Anton Schneider (1868): About the construction and development of Polygordius. Archives for Anatomy, Physiology and Scientific Medicine, 1868, pp. 51–60, panels II – III.
- Voldemar Czerniavsky (1881): Materialia ad Zoographiam Ponticam Comparatam. Fasciculum III. Vermes. Bulletin de la Société Impériale des Naturalistes de Moscou. 55 (4): 213-344, here S. Fam. 2. Polygordidae, nov. fam., gen. 2. Polygordius, Schneider. P. 285.
- John Percy Moore (1904): A new generic type of Polygordidae. American Naturalist 38 (451), pp. 519-520.
- E. Rota, G. Carchini (1999): A new Polygordius (Annelida: Polychaeta) from Terra Nova Bay, Ross Sea, Antarctica. Polar Biology 21, pp. 201-213.
- Marian Hope Pettibone: Annelida. In: Sybil P. Parker (Ed.): Synopsis and Classification of Living Organisms , Vol. 2, pp. 1-43. McGraw-Hill, New York 1982. p. 40, Polygordiida.
- Stanley J. Edmonds: Fauna of Australia, Volume 4A. Polychaetes & Allies. The Southern Synthesis 4. Commonwealth of Australia, 2000. Class Polychaeta. P. 317, Family Polygordiidae.
Web links
- Polygordiidae . In: Lexicon of Biology , online edition.
Individual evidence
- ↑ Polygordius Schneider, 1868 WoRMS , 2018. Accessed November 15, 2018th