Pomeranz-Fritsch reaction
The Pomeranz-Fritsch reaction , also known as the Pomeranz-Fritsch cyclization , is a name reaction in organic chemistry and was independently discovered in 1893 by the German chemist Paul Fritsch (1859–1913) and the Austrian chemist Cäsar Pomeranz (1860–1926). It is a reaction for the synthesis of isoquinoline and its derivatives .
Overview reaction
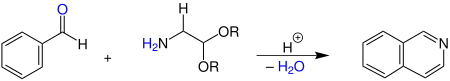
In the classic Pomeranz-Fritsch reaction, benzaldehyde is converted to isoquinoline with a 2,2-dialkoxyethylamine in the presence of an acid .
Various alkyl groups can be used for the radicals R in the reaction , e.g. B. methyl and ethyl groups .
In the original work, concentrated sulfuric acid was used as the source of protons. However, variants with Lewis acids are also known today. Any substituted isoquinolines can be synthesized by using various aromatic aldehydes or ketones .
mechanism
A possible reaction mechanism for the Pomeranz-Fritsch reaction is as follows:
If benzaldehyde and 2,2-dialkoxyethylamine are heated, they condense with elimination of water to form intermediate 1 . One of the two alkoxy groups is protonated by adding acid . Then an alcohol splits off. With elimination of a proton, the ether 2 is formed through ring closure . In the next step, the remaining alkoxy group is also protonated and split off. Isoquinoline is formed through rearomatization with the release of a proton.
application
The Pomeranz-Fritsch reaction has numerous applications in the chemical industry. It is an effective method, especially for direct isoquinoline synthesis. Isoquinoline is an important intermediate for the synthesis of various important derivatives.
These are used in a variety of ways, such as:
- Anesthetics such as dimethisoquine .
- Antihypertensives such as quinapril , Quinapirilat and debrisoquine. All derivatives of 1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinoline.
- Fungicides such as 2,2'-hexadecamethylenediisoquinolinium dichloride, which is also an antiseptic .
- Disinfectant N -Laurylisoquinolinium bromide
- Vasodilators such as papaverine
In addition, isoquinoline derivatives are used in the manufacture of dyes, insecticides, antifungal agents and corrosion inhibitors.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b C. Pomeranz: About a new isoquinoline synthesis . In: Monthly books for chemistry and related parts of other sciences . tape 14 , no. 1 , December 1893, p. 116-119 , doi : 10.1007 / BF01517862 .
- ↑ a b c Paul Fritsch: Syntheses in the isocoumarin and isoquinoline series . In: Reports of the German Chemical Society . tape 26 , no. 1 , 1893, p. 419-422 , doi : 10.1002 / cber.18930260191 .
- ↑ a b c Zerong Wang: Comprehensive Organic Name Reactions and Reagents . John Wiley & Sons, New Jersey 2009, ISBN 978-0-471-70450-8 , pp. 2256-2259 .
- ↑ a b c László Kürti and Barbara Czakó .: Strategic Applications of Named Reactions in Organic Synthesis: Background and Detailed Mechanisms . Elsevier Academic Press, 2005, ISBN 978-0-12-429785-2 , pp. 358-359.
- ^ A b Jie Jack Li: Name Reactions - A Collection of Detailed Reaction Mechanisms , Springer, 2006, ISBN 978-3-540-30030-4 , pp. 472-474.