Red diamond rattlesnake
| Red diamond rattlesnake | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

Red diamond rattlesnake ( Crotalus ruber ) |
||||||||||||
| Systematics | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| Scientific name | ||||||||||||
| Crotalus ruber | ||||||||||||
| Cope , 1892 |
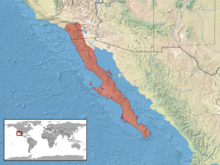
The red diamond rattlesnake ( Crotalus ruber ) is a species of rattlesnakes ( Crotalus ), whose distribution area from southern California to the to Mexico is part of Baja California expands.
features
The red diamond rattlesnake is a large and powerfully built rattlesnake with an average body length of over one meter, with individual individuals up to 1.50 meters long. The typical basic color is red-brown to brick-red, but it can also be olive-green or brown (especially in the southern parts of the distribution area, subspecies C. r. Lucasensis ). The drawing consists of large diamonds , which are usually bordered in white. These white borders are only missing on some island shapes. The head is marked by a wide red or brown temple band that leads over the eyes to the corners of the mouth and can also be framed in white. The tail has a black and white banding made up of narrow bands, which contrasts strongly with the body, especially in red-brown animals.
distribution and habitat
The range of the snake extends from southern California to the to Mexico is part of Baja California and excludes only the driest areas in the desert. The species is also found on some islands in the Gulf of California .
The snake's habitat is characterized by arid desert areas, with the snake mainly found in areas with stony ground or sparse vegetation.
Snake venom
The venom of this snake is essentially the same as that of the Texas rattlesnake ( C. atrox ) and accordingly has above all hemotoxic components, which are composed of tissue-destroying proteins. The effect consists mainly of tissue destruction, local painful swellings and hemorrhagic effects.
Systematics
Three subspecies of the red diamond rattlesnake are currently considered valid:
- C. r. lorenzoensis endemic to the island of San Lorenzo Sur ; this subspecies is smaller than the animals on the mainland and tends to reduce the tail rattle due to the loss of the last rattle segments
- C. r. lucasensis in the Cape region of Baja California south of Loreto ; it is brown to olive green and is considered to be more aggressive than the nominate form
- C. r. ruber in southern California and most of Baja California with the exception of the Cape region.
literature
- Chris Mattison: Rattlers! - A natural history of rattlesnakes. Blandford, London 1996; P. 120; ISBN 0-7137-2534-6
Web links
- Crotalus ruber in The Reptile Database
- Crotalus ruber inthe IUCN 2013 Red List of Threatened Species . Posted by: Hammerson, GA, Frost, DR & Hollingsworth, B., 2007. Retrieved October 5, 2013.