Threshold switch
A threshold switch is an electronic or electrical component that combines the function of a sensor with a switching function. The switching process is triggered when the physical variable measured by the sensor exceeds or falls below a preset limit value (the threshold value ).
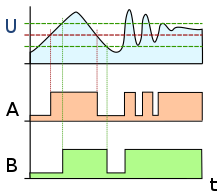
A hysteresis is usually built in to avoid unwanted (e.g. too fast or too frequent) repetitions of switch-on and switch-off processes if the measured variable fluctuates slightly around the threshold value. For this it is necessary that the upper and lower switching thresholds are adapted to the respective circumstances in such a way that the fluctuations to be suppressed take place between these two threshold values. It is only switched on when the upper switching threshold is exceeded, and only when the lower switching threshold is not reached is switched off, and values in between do not result in any switching operations. The switching function can also be designed to be inverted , so that the on / off behavior is reversed.
Electronic threshold value switches (initiator circuits) are, for example, Schmitt triggers ; they are available individually or in groups as an integrated circuit . They react to a slow change in the input voltage with a sudden change in the switching state (logical state) at the output.
Even Hall -circuits often have a digital output with hysteresis behavior against the change of the magnetic field.
Proximity switches in automation technology react to the approach of metal parts or other surfaces by triggering a switching action ( relay or transistor switch at the output).
Another example of a threshold switch with hysteresis is deep discharge protection for a battery. This switches off the connected consumers when the voltage falls below a threshold value. This protects the battery from excessive discharge. However, due to the internal resistance of the battery, the terminal voltage dropped when it was loaded. If no current flows, the voltage rises again and reaches the open circuit voltage. Without hysteresis, this would lead to quick and undesired switching on and off. Therefore, a slightly higher restart voltage is specified. This is only achieved by recharging the battery.
swell
- Schmitt trigger or threshold switch Saxon education server ( Memento from 23 August 2010 in the Internet Archive )
- Wilfried Plaßmann, Detlef Schulz (Hrsg.): Handbook of electrical engineering. 5th edition Vieweg + Teubner Verlag , 2008, ISBN 978-3-8348-0470-9 , p. 419 ( limited preview in the Google book search)