Somali runner lark
| Somali runner lark | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Systematics | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| Scientific name | ||||||||||||
| Alaemon hamertoni | ||||||||||||
| Witherby , 1905 |
The Somali runner lark ( Alaemon hamertoni ) is a species of the lark family. Their distribution area is in the east of Africa. It is a skylark-sized, long-legged lark that resembles a pipit in its habitus . They are able to move very quickly on the ground. There are three subspecies.
The IUCN classifies the population of the Somali runner lark as harmless (least concern).
features
The Somali runner lark reaches a body length of about 18 to 20 centimeters, of which the male has between 6.75 and 7.45 centimeters and the female 6.1 to 6.27 centimeters on the tail. The beak measures between 1.9 and 2.15 centimeters from the skull in males, while in females it is between 1.7 and 1.9 centimeters. Apart from the size difference, there is no noticeable gender dimorphism .
The upper side of the body of the Somali runner lark is a single color from sand-brown to gray-brown, with the coat a little darker and the rump the lightest. The upper tail covers are light yellow-brown and also have no other colored markings. The over-eye stripe is short and light, the ear covers are gray to sandy brown. The chin and throat are white, the throat is finely speckled with gray, the cream-white breast, on the other hand, is slightly more speckled and has individual brownish dots. The rest of the underside of the body is cream-colored to white. The hand and arm wings are gray-brown, the individual feathers are lined with narrow yellow-brown. The wings also have whitish tips. The tail is brown to dark brown. The middle pair of control springs is slightly lighter than the other control springs and has a slightly reddish tone. The shaft line is dark. All control springs have a narrow, light-colored border. The beak is dark horn-colored. The rear toe is short and, unlike the sandpiper lark belonging to the same genus, elongated. The iris is brown.
Possible confusion
Due to its habitus, the Somali runner lark can be confused with the brown-backed pipit found in the same range . The Somali runner lark can be distinguished from the stone lark by its significantly slimmer beak.
Distribution area and habitat
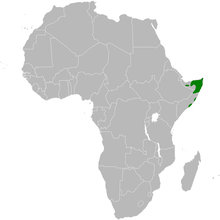
The Somali runner lark is found in northeast Somalia. Their living space is open grassy areas. It is a resident bird in the entire distribution area.
Way of life
The living habits of the Somali runner lark have so far only been examined very superficially. Like all larks, however, it is a ground breeder. The nests found so far were in earth hollows. The eggs have an ivory-white basic color and have a dense pattern of reddish and earth-colored spots and blobs.
Subspecies
There are three subspecies:
- A. a. age - Witherby , 1905 : North and Northeast Somalia
- A. a. tertius - Clarke, S , 1919 : Occurrence in the northwest of Somalia
- A. a. hamertoni - Witherby, 1905 : nominate form, occurrence in central Somalia
literature
- Rudolf Pätzold: The larks of the world . Westarp Sciences, Magdeburg 1994, ISBN 3-89432-422-8 .
- Rudolf Pätzold: Compendium of Larks. All the larks on earth. Jan-Schimkat-Medienpublikation, Dresden 2003, ISBN 3-00-011219-7 .
Web links
Single receipts
- ↑ a b Pätzold: Compendium of Larks . P. 211.
- ^ Pätzold: Compendium of Larks . P. 209.
- ^ Pätzold: Compendium of Larks . P. 210.
- ^ IOC World Bird List 6.4 . In: IOC World Bird List Datasets . September. doi : 10.14344 / ioc.ml.6.4 .