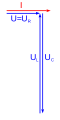
Excess voltage
Of excessively high voltage is used when the voltage across a coil or a capacitor has reached a higher value than the total voltage.
This effect occurs in a series resonant circuit . There, the same current flows in the coil and capacitor due to the series connection , but the sinusoidal voltages have a phase shift of π in radians . This is made up of the phase shift of the coil from minus the phase shift at the capacitor of .
This effect can be used by specifying the total voltage and tapping the voltage across one of the two energy stores. To calculate the voltage, the circuit can be viewed as a complex voltage divider ( see resonance transformer ).
The voltage increase is greatest with resonance and in this case proportional to the quality factor , i.e. with an oscillating circuit of quality 100, with resonance and an input voltage of one volt, reactive voltages of 100 V are achieved on the capacitor and on the coil. This effect is used in laptops to use a resonance converter to generate around 700 V AC from a low DC voltage of 12 V to operate the fluorescent tube .
Vector diagram of a series resonant circuit below the resonance frequency
Related topics
The counterpart in the parallel resonant circuit is the current increase .