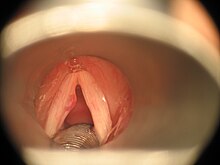
Vocal fold polyp
| Classification according to ICD-10 | |
|---|---|
| J38.1 | Polyp of the vocal folds and larynx |
| ICD-10 online (WHO version 2019) | |
A vocal fold polyp or vocal cord polyp is a benign change in a vocal fold that occurs exclusively on the free edge or on the subglottic slope of the anterior third of the vocal fold. Small vocal fold polyps are broad-based, larger ones are spherical, stalked, they mostly only occur on one side (90%).
A distinction is made between reddish telangiectatic , vascularized vocal fold polyps and glassy gelatinous polyps. Malignant degeneration of vocal fold polyps has not been described.
Definite causes for the development of vocal fold polyps are not known, they occur mainly in middle age, more often in men and cigarette smokers. It is also noticeable that these patients often make particular demands on their voices.
Symptoms
Vocal cord polyps cause a more or less pronounced hoarseness or Diplophonie (Doppeltönigkeit of the vocal sound). With larger polyps hanging in the subglottic space, the hoarseness can be intermittent, but disappears again after clearing the throat or coughing . Choking attacks are also possible with larger polyps.
diagnosis
The diagnosis is made by an ENT doctor using a laryngoscopy . Small polyps cannot be differentiated from vocal cord nodules or cysts when mirrored .
therapy
Treatment consists of microlaryngoscopic surgical removal of the polyp. The vocal fold level is adjusted over the mouth with an operating laryngoscope and the polyp is removed with small instruments or with a laser under a microscopic view . An ablation under local anesthesia is also possible with specialized phonosurgeons . As always, the removed (tiny) piece of tissue is examined histologically for the final diagnosis. A relapse is extremely rare in vocal cord polyp.
literature
- Kleinsasser O .: Microlaryngoscopy and endolaryngeal microsurgery. Technique and typical findings. Schattauer, 1998.