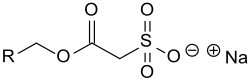
Sulfoacetates
Sulfoacetates are a class of anionic surfactants whose sodium salts are very good foaming agents with high foam stability and, with small amounts of sodium chloride, cause a pronounced increase in the viscosity of aqueous detergent solutions .
The chain length of the hydrophobic part of the molecule R is between R = C 6 and C 20 . Mostly, lauryl alcohol C 12 or a mixture of lauryl and myristyl C 14 from the principal fatty acids of the coconut oil used. As mild and well biodegradable surface-active compounds are Sulfoacetate use in shampoos and liquid soaps , as well as in the locally effective laxative Microlax R .
Manufacturing
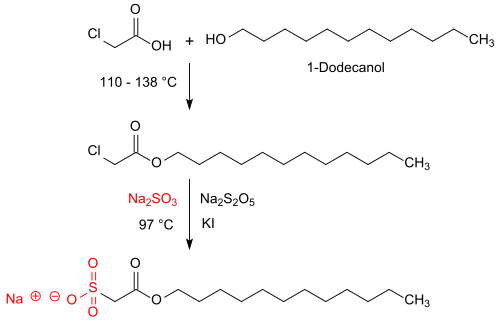
The synthesis of sulfoacetates takes place in two reaction stages. In the first stage, a long-chain fatty alcohol (> C 8 chain length, such as 1-dodecanol ) or a fatty alcohol mixture reacts when heated with monochloroacetic acid to temperatures of up to 140 ° C with elimination of water to form the corresponding chloroacetic acid ester, such as. B. dodecyl 2-chloroacetate. This intermediate compound is also obtained as a light yellow oil in 95% yield by reacting lauryl alcohol with chloroacetic acid chloride .
In the second reaction stage, the chloroacetic acid ester is heated to temperatures of 90 to 97 ° C for 11 hours with a 33% excess of sodium sulfite Na 2 SO 3 and additionally sodium disulfite Na 2 S 2 O 5 as a buffer and potassium iodide KI as a catalyst. The sulfoacetate is formed as a sodium salt in addition to sodium chloride and sodium sulfate , the inorganic salts mostly remaining in the end product, which is adjusted to an active ingredient concentration of 65 or 85% by adding salt.
The aim of the reaction is to generate the smallest possible residual amounts of the strongly corrosive and toxic reactant monochloroacetic acid and the sodium monochloroacetate (if possible <5 ppm) formed during the reaction with sodium sulfite, with as complete a conversion of the fatty alcohol as possible, since subsequent purification of the sulfoacetate thus produced in the Usually not done.
Properties and use
Sulfoacetates are particularly mild surfactants with little irritation to the skin and mucous membranes and are therefore mostly used in shampoos, liquid soaps and foam baths. As emulsifiers, they cause rapid surface wetting , reduction of surface tension and the formation of fine-bubble, creamy and stable foam.
Contrary to popular belief, the tendency of a surfactant to form a lot of foam does not correlate with increased fat dissolving and cleaning power; mostly the opposite is the case. As a rule, the solubilization capacity of surface-active compounds of the same chain length in the hydrophobic part of the molecule is: nonionic> cationic> anionic.
Sulphoacetates are almost neutral in aqueous solution (pH 6.3 in 1% solution), easily biodegradable and hydrolytically stable over a wide pH range. They are stable against hard water, i.e. H. they do not form any undesired precipitates from poorly soluble calcium salts and, when sodium chloride is added, they drastically increase the viscosity of surfactant preparations, which suggests to the consumer a higher concentration of active ingredients and thus cleaning performance. In addition to their use in skin-friendly body care products, sulfoacetates are also used in oral care products such as: B. toothpaste and mouthwashes, as well as lubricants in locally effective laxatives such as Microklist R are used.
The consumer preference for high-foaming shampoos and liquid soaps, which also have a less degreasing effect than the anionic surfactant class of fatty alcohol sulfates , such as. B. sodium lauryl sulfate SLS or the alkyl ether sulfates , such as. B. Sodium dodecyl poly (oxyethylene) sulfate and are also “ sulfate -free” and “EO-free”, opens up future potential for mild and readily biodegradable surfactants, such as. B. for sulfoacetates, sulfosuccinates and sulfobetaines, as well as for amphoacetates , isethionates , taurides or acylglutamates.
Individual evidence
- ↑ Patent US5616782 : Method of producing alkyl sulfoacetate compositions. Filed November 16, 1995 , published April 1, 1997 , Applicant: Stepan Co., Inventors: R. Thompson, NM Rockwell, AM Michels, WR Mohring, KC Kolbe, JD Seibold, JM Butterwick.
- ↑ AK Ressmann, R. Zirbs, M. Pressler, P. Gaertner, K. Bica: Surface-active ionic liquids for micellar extraction of piperine from black pepper . In: Z. Naturforsch. 68b, 2013, p. 1129–1137 , doi : 10.5560 / ZNB.2013.3196 .
- ↑ Lathanol LAL, Product Bulletin. (PDF; 54 KB) In: stepan.com. Stepan Company, accessed June 22, 2018 .
- ^ PA Cornwell: A review of shampoo surfactant technology: consumer benefits, raw materials and recent developments . In: Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. tape 40 , 2018, p. 16-30 , doi : 10.1111 / ics.12439 ( wiley.com [PDF]).
- ^ Stepan Personal Care Specialty Surfactants. (PDF; 1.56 MB) In: stepan.com. Stepan Company, accessed June 22, 2018 .