Chloroacetic acid chloride
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
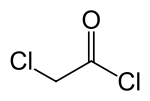
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Chloroacetic acid chloride | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 2 H 2 Cl 2 O | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless to yellowish, pungent smelling liquid |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 112.94 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
liquid |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
1.42 g cm −3 |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
−22.5 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
105-110 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
25.3 h Pa (at 20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
decomposes in water |
|||||||||||||||
| Refractive index |
1.452-1.454 |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| MAK |
Switzerland: 0.05 ml m −3 or 0.24 mg m −3 |
|||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||
| Thermodynamic properties | ||||||||||||||||
| ΔH f 0 |
−283.7 kJ / mol |
|||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | ||||||||||||||||
Chloracetic acid chloride is a chemical, more precisely the simply chlorinated form of acetic acid chloride . The colorless to slightly yellowish, pungent smelling liquid smokes in moist air.
Extraction and presentation
Can be obtained chloroacetic acid chloride by chlorination of chloroacetic acid with phosphorus trichloride , thionyl chloride , sulfuryl chloride or phosgene . Alternatively, vinylidene chloride can be reacted with oxygen in the presence of radical initiators (chlorine, UV light) in the vapor phase to form chloroacetic acid chloride.
properties
Chloracetic acid chloride reacts with water to form monochloroacetic acid and hydrogen chloride .
use
Chloracetic acid chloride is an important building block for the synthesis of organic compounds, e.g. B. pesticides, adrenaline , diclofenac , diazepam or lidocaine .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g h Entry on chloroacetyl chloride in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on January 10, 2017(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ Entry on chloroacetic acid chloride at ChemBlink , accessed on February 25, 2011.
- ↑ Entry on Chloroacetyl chloride in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on February 1, 2016. Manufacturers or distributors can expand the harmonized classification and labeling .
- ↑ Swiss Accident Insurance Fund (Suva): Limit values - current MAK and BAT values (search for 79-04-9 or chloroacetic acid chloride ), accessed on November 2, 2015.
- ↑ a b c Toxicological assessment of chloroacetyl chloride (PDF) at the professional association raw materials and chemical industry (BG RCI), accessed on August 22, 2012.
- ↑ David R. Lide (Ed.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . 90th edition. (Internet version: 2010), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, Standard Thermodynamic Properties of Chemical Substances, pp. 5-21.
- ↑ Patent US3674664 : Method of preparing chloroacetyl chloride. Filed March 6, 1970 , published July 4, 1972 , Applicant: The Dow Chemical Company, Inventor: Albert Kent Keller, Eric R. Larsen, Raymond A. Plepys.



