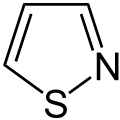
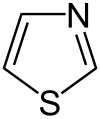
Thiazoles
Thiazoles are a chemical group from the field of heterocyclic compounds and belong to the group of azoles . Its members are five-membered cyclic organic compounds with a sulfur and a nitrogen atom in the ring structure. The parent systems are thiazole and isothiazole , with the two heteroatoms in isothiazole being adjacent and in thiazole a carbon atom between them.
presentation
Isothiazoles can be synthesized by reacting iminothioamides with chloramine .
The synthesis of thiazoles is achieved by the condensation of α- halogenated carbonyls with thioamides.
Thiazoles can also be synthesized by the oxidation of 3-thiazolines with sulfur.
Derivatives
3-thiazolines (synonym: tetrahydrothiazoles) can also be regarded as derivatives of thiazoles.
Individual evidence
- ^ A b David T. Davies: Basic Texts Chemistry, Vol. 1: Aromatic Heterocyclen . 1st ed. Wiley-VCH, Weinheim 1995, pp. 10-34, ISBN 3-527-29289-6 (Oxford Chemistry Primers).
- ↑ Friedrich Asinger , Manfred Thiel, Lothar Schröder: About the joint action of elemental sulfur and gaseous ammonia on ketones VII. The dehydration of thiazolines-Δ 3 to thiazoles , Liebigs Ann. Chem. , Vol. 610 (1957), pp. 49-56, doi : 10.1002 / jlac.19576100106 .