Thymoma
| Classification according to ICD-10 | |
|---|---|
| D15.0 | Benign neoplasm of the thymus |
| C37 | Malignant neoplasm of the thymus |
| ICD-10 online (WHO version 2019) | |
Thymoma is the medical term for a tumor of the thymus (German also called Bries). About three quarters of these tumors are benign and only one quarter are malignant. The malignant ones are called malignant thymoma or thymic carcinoma . In a more distant sense, the thymus carcinoid, as a tumor within the thymus, is one of the malignant thymus tumors.
Symptoms
About 30% of patients are asymptomatic at the time of diagnosis. Symptoms can include coughing, chest pressure, or shortness of breath.
Occasionally, a thymoma can also be identified by a paraneoplastic syndrome . Myasthenia gravis is found in 25% of all thymomas , but polymyositis , arthritis or Sjogren's syndrome , erythrocyte aplasia , giant cell myocarditis , hypogammaglobulinemia , autoimmune movement disorders and other autoimmune diseases can also occur. The cause is often the lack of gene expression of the autoimmune regulator gene ( AIRE ), which increases the normal elimination of autoreactive T lymphocytes in the thymus.
A thymus carcinoid can be suspected by the carcinoid-typical triad of diarrhea , flush (blushing) and cardiac complaints.
Diagnosis
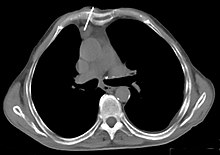
Indications of a thymoma are already evident in the chest x-ray in the presence of an unclear anterior mediastinal mass . It is one of the mnemonic often cited four T's in the differential diagnosis of anterior mediastinal masses ( T eratom , T hymom, parotid t hyroidea and " t errible lymphoma" ). Computed tomography (CT) is part of the standard diagnosis. To distinguish between benign and malignant tumors, it is always necessary to take a tissue sample ( biopsy ) and examine it with a fine tissue.
In the WHO classification, the following is divided according to the morphological appearance of the epithelial cells:
- Type A - the epithelial cells are predominantly oval or spindle-shaped and resemble the normal medullary epithelial cells of the thymus
- Type B - the epithelial cells are predominantly round or polygonal and resemble the normal cortical epithelial cells of the thymus. Depending on the severity of the cytological atypia , types B1, B2 and B3 are distinguished.
- Type C - thymic carcinoma
Individual evidence
- ↑ IG Schmidt-Wolf, JK Rockstroh, H. Schüller et al .: Malignant thymoma: current status of classification and multimodality treatment. In: Ann Hematol. 82 (2), 2003, pp. 69-76. PMID 12601482 .
- ↑ Margaret Seton, Carol C. Wu, Abner Louissaint: Case 26-2013 - A 46-Year-Old Woman with Muscle Pain and Swelling . In: New England Journal of Medicine . 2013, Volume 369, Issue 8 of August 22, 2013, pp. 764-773; doi: 10.1056 / NEJMcpc1208152 .