Thyronamines
Thyronamines (abbreviation TAM ) are a class of endogenous signaling substances that are structurally related to the thyroid hormones . Thyronamine and its iodine- substituted derivatives are representatives of the substance class .
Structure and nomenclature
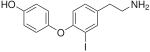
The thyronamines differ from the thyroid hormone thyroxine (T 4 ) and its deiodinated derivatives in the absence of the carboxyl group in the alanine side chain of the diphenyl ether backbone. The basic structure is the thyronamine (T 0 AM), a 4-phenoxyphenol with an ethylamine side chain:
The substance class includes nine compounds with different numbers and positions of iodine substituents. They are briefly referred to as T x AM, where x stands for the number of iodine substituents.
Occurrence and characteristics
Two representatives could be detected in vivo - besides thyronamine (T 0 AM), 3-iodothyronamine (3-T 1 AM). Both compounds were found in the blood , heart , liver , adipose tissue , thyroid gland and brain of adult male mice, as well as in the brains of various other species such as e. B. Rats and guinea pigs detected. The compounds of this class of substances are synthesized in the body from the thyroid hormones thyroxine (T 4 ) and triiodothyronine (T 3 ). First T 4 (thyroxine) is converted to T 3 by deiodination and this is then converted to thyronamine by decarboxylation of the alanine residue.
Interestingly, thyronamines do not bind to the thyroid hormone receptor (a nuclear receptor), but to a G-protein-coupling receptor (i.e. a membrane receptor), despite their high structural similarity to thyroid hormone . For T 1 AM it was shown that it is a receptor of the TAAR family (trace amine associated receptor).
In experiments with mice it was shown that T 1 AM and T 0 AM are able to significantly lower both heart rate and body temperature. This effect can be reversed by administering isoproterenol .
Individual evidence
- ↑ S. Piehl, CS Höfig, TS Scanlan, J. Köhrle: Thyronamines-Past, Present, and Future . In: Endocrine Reviews . tape 32 , no. 1 , February 1, 2011, p. 64 , doi : 10.1210 / er.2009-0040 .
- ↑ External identifiers or database links for thyronamine : CAS number: 500-78-7, PubChem : 3083601 , ChemSpider : 2340781 , Wikidata : Q419754 .
- ↑ External identifiers of or database links to 3,3 ', 5-triiodothyronamine : CAS number: 4731-88-8, PubChem : 165262 , ChemSpider : 144879 , Wikidata : Q4634051 .
- ↑ External identifiers or database links for 3-iodothyronamine : CAS number: 712349-95-6, EC number: 685-805-0, ECHA InfoCard: 100.211.501 , PubChem : 9950514 , ChemSpider : 8126125 , Wikidata : Q2815997 .
- ↑ Thomas S Scanlan, Katherine L Suchland, Matthew E Hart, Grazia Chiellini, Yong Huang, Paul J Kruzich, Sabina Frascarelli, Dane A Crossley, James R Bunzow, Simonetta Ronca-Testoni, Emil T Lin, Daniel Hatton, Riccardo Zucchi, David K Grandy: 3-Iodothyronamine is an endogenous and rapid-acting derivative of thyroid hormone . In: Nature Medicine . tape 10 , no. 6 , June 2004, p. 638 , doi : 10.1038 / nm1051 .