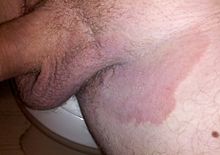
Tinea inguinalis
| Classification according to ICD-10 | |
|---|---|
| B35.9 | Tinea onA |
| ICD-10 online (WHO version 2019) | |
Tinea inguinalis or inguinal lichen - incorrectly referred to as tinea cruris in the Anglo-American language area , which literally means 'lower leg lichen' - is a dermatophytosis of the groin area , in men also of the scrotum area . Disease triggers are dermatophytes . The classic pathogen is Epidermophyton floccosum , but Trichophyton rubrum is more common today . Other triggers are Trichophyton mentagrophytes and Trichophyton tonsurans . Tight, airtight clothing, which leads to a warm, humid microclimate in this region, has a positive effect.
The fungal disease usually shows up as redness with itching. Scales , papules, or pustules can also appear on the edge . The spread usually takes place in the periphery of the skin lesion while it begins to heal centrally.
Treatment is usually done locally with antifungal agents .
literature
- Otto Braun-Falco , Gerd Plewig , Helmut H. Wolff, Walter HC Burgdorf, Michael Landthaler: Dermatology and Venereology. 5th edition. Springer, Berlin et al. 2005, ISBN 3-540-40525-9 , pp. 187-188.
Individual evidence
- ↑ Peter Altmeyer , Martina Bacharach-Buhles: Springer Encyclopedia Dermatology, Allergology, Environmental Medicine. Springer, Berlin et al. 2002, ISBN 3-540-41361-8 , p. 1580.