Enterprise application integration
Enterprise Application Integration ( EAI ) and enterprise application integration ( UAI ) is a concept for enterprise-wide integration of business functions along the value chain that are distributed across different applications on different platforms and in terms of data and business processes are integration-related. The aim is integrated business processing through a network of internal company applications of different generations and architectures.
The different methods
- Data integration , enterprise bus ,
- Application integration, message broker and
- Process integration , process management tool
build on each other.
Definition of terms
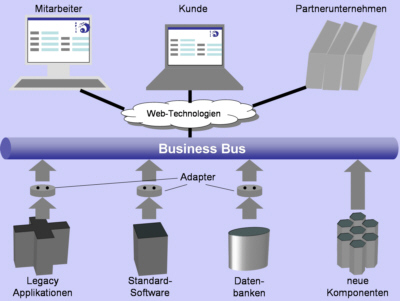
EAI comprises the planning , the methods and the software to integrate heterogeneous, autonomous application systems - possibly with the inclusion of external application systems - in a process-oriented manner. EAI is thus the process-oriented integration of application systems in heterogeneous IT application architectures .
In contrast to other integration techniques , such as function integration or data integration , the EAI approach does not change the implementation of the individual business functions. All functional interfaces are abstracted using adapters (interface converters).
On the connecting business bus (also known as EAI backbone, integration bus or integration platform), dynamically evaluated rules and process descriptions ensure that the data of a business case is transferred to the individual functions in the correct sequence and the results are forwarded.
Essential for this type of integration , which can also be coupled as a loose (engl. Loosely coupled ), is the strict separation of business process logic and business functions. For this purpose, the individual business processes are broken down into macro and micro processes. The micro-processes are partly integrated into the functions, since they cannot be separated out, especially when using standard software.
In contrast to the pure interface adaptation through classic middleware , EAI also offers the option of mapping business process logic . However, this is also possible in many modern middleware products through the integration of a business process engine .
Due to the process-oriented integration, EAI is not only a technical integration platform, but - at least according to the conceptual claim - also an integration component between the organizational architecture with the structures and business processes and the IT architecture of a company.
Action
For the implementation of similar tasks of enterprise application integration, samples were suggested. A collection of such patterns can be found in the book Enterprise Integration Patterns by Gregor Hohpe and Bobby Wolf.
Differentiation from SOA
EAI can be understood as the predecessor of the service-oriented architecture (SOA). The technological concepts for connecting the application landscape to a central communication component, the message broker, are similar. However, SOA requires that the connected applications follow the service paradigm, whereas in the EAI scenario they can remain untouched.
Areas of application
EAI is used in practically all areas of process integration, especially in e-business and in portals , as it is a prerequisite for the necessary straight through processing . In addition, EAI is replacing classic middleware products in many large companies with complex IT landscapes and is becoming an important IT architecture element.
species
In practice a distinction is made here
- Application to Application Integration ( A2A ): The integration at the system level. A hub-spoke architecture ( hub and spoke ) or a bus architecture can be used. The classic peer-to-peer architecture is not integration in the sense of enterprise application integration, but what you want to avoid with EAI.
- Person to System Integration (P2S): Providing several applications with a common user interface .
- Business to Business Integration (B2B): The integration of applications across company boundaries.
- Total Business Integration (TBI): The summary of all types of integration.
See also
- Enterprise application management
- Enterprise content management
- Enterprise Resource Planning
- Data warehouse
- OSGi
- Web service (can be used at EAI)
- Workflow management
literature
- OSGi Service Platform. Release 3. IOS Press, 2003, ISBN 1-58603-311-5 (English)
- Service-Oriented Architecture . IBM Systems Journal edition on SOA. 12 scientific papers on SOA
- Stephan Aier, Marten Schönherr (Hrsg.): Enterprise Application Integration - Flexibilization of Complex Enterprise Architectures . 2nd Edition. Gito, Berlin 2007, ISBN 3-936771-17-0 (Enterprise Architecture, Volume 1)
- Stephan Aier, Marten Schönherr (ed.): Enterprise Application Integration. Service orientation and sustainable architectures. 2nd Edition. Gito, Berlin 2006, ISBN 3-936771-74-X (Enterprise Architecture, Volume 2)
- Sven-Carsten Strüver: Standard-based EAI procedure using the example of investment banking. Gito, Berlin 2006, ISBN 978-3-936771-81-7
- Knut Hildebrand: IT integration & migration. Dpunkt Verlag, Heidelberg 2007, ISBN 978-3-89864-455-6 .
- Michael Kaib: Enterprise Application Integration. Deutscher Universitäts-Verlag, Wiesbaden 2002, ISBN 3-8244-2163-1
- Wolfgang Keller: Enterprise Application Integration. dpunkt Verlag, Heidelberg 2002, ISBN 3-89864-186-4
- David Linthicum: Enterprise Application Integration. Addison-Wesley, 2000, ISBN 0-201-61583-5
- Kersten Bassow: ISIS Enterprise Application Integration REPORT. Nomina GmbH, Munich 2005, ISBN 3-936090-88-2
- Susanne Leist, Robert Winter (Ed.): Retail banking in the information age. Springer, Berlin / Heidelberg 2002, ISBN 3-540-42776-7
- Stefan Conrad, Wilhelm Hasselbring, Arne Koschel, Roland Tritsch: Enterprise Application Integration - Basics, Concepts, Design Patterns, Practical Examples. Spektrum, Munich, 2005, ISBN 3-8274-1572-1
Individual evidence
- ↑ Gregory Hohpe, Bobby Woolf: Enterprise Integration Patterns . Designing, Building, and Deploying Messaging Solutions. Addison-Wesley, 2003, ISBN 978-0-321-20068-6 ( eaipatterns.com [accessed April 16, 2013]).