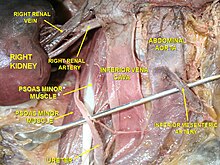
Inferior vena cava

The inferior vena cava ("lower vena cava ") is a strong venous blood vessel in the chest and abdominal cavity . In animals, it is called the caudal vena cava ("posterior vena cava").
The inferior vena cava arises from the confluence of the two common iliac veins in the lumbar region and runs towards the diaphragm . It passes through the vena cava hole ( foramen venae cavae ) through the diaphragm and runs in its own pleural fold ( plica venae cavae ) to the right atrium of the heart . At the level of the abdominal cavity, it absorbs the blood from the kidney, testicular / ovarian and lumbar veins. The blood of the unpaired abdominal organs, on the other hand, first reaches the portal vein and is only conducted into the inferior vena cava via the liver veins after passing through the liver shortly before it passes through the diaphragm .
Azygos continuity is rarely found as a malformation .