Xylenol blue
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
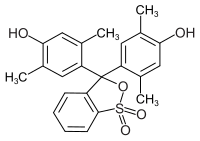
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Xylenol blue | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 23 H 22 O 5 S | |||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 410.48 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
212 ° C (decomposition) |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Xylenol blue is a triphenylmethane dye and belongs to the group of sulfonphthaleins. It is used as a pH indicator . Its phthalein analogue is xylenolphthalein . The bromoxylenol blue can be represented by bromination .
properties
There are two areas of color change:
- pH 1.2-2.8: color change from red to yellow
- pH 8.0-9.8: color change from yellow to purple
Xylenol blue contains two hydroxyl groups and an unstable sultone ring . This ring is split in an aqueous medium, and after a rearrangement the quinoid yellow colored form of the dye is formed. In a strongly acidic environment (pH <1.2) the quinoid system is protonated, which causes the solution to turn red. In a basic environment (pH = 8.0-9.8) the hydroxyl group is deprotonated and the solution turns purple.
use
Xylenol blue is used as an indicator in acid-base titrations. In most cases, only the second transition range (pH = 8.0–9.8) is used for the indication.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d Xylenol Blue data sheet from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on April 25, 2011 ( PDF ).
