Zygoballus sexpunctatus
| Zygoballus sexpunctatus | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

Zygoballus sexpunctatus , male |
||||||||||||
| Systematics | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| Scientific name | ||||||||||||
| Zygoballus sexpunctatus | ||||||||||||
| ( Hentz , 1845) |
Zygoballus sexpunctatus is a species of jumping spider whose range is restricted to the eastern United States of America .
description
Adult females of Z. sexpunctatus are between 3.5 and 4.5 mm long, while the males are between 3 and 3.5 mm long. The prosoma is copper-colored, red-brown to black with numerous white scales on the clypeus . Viewed from above, the cephalothorax appears roughly square. The chelicerae of the males are greatly enlarged and oriented obliquely, with each chelicerae being equipped with a prominent inner tooth and a long, curved claw. The back eyes are raised, the thorax drops steeply behind the head. The opisthosoma is dark brown to black with a white basal band and two white horizontal stripes. These are usually interrupted and form the six eponymous spots of the species. However, some or all of the spots may be missing. The legs are reddish-brown with the femur of the front leg being darker and enlarged.
Z. sexpunctatus resembles the species Zygoballus rufipes , with which it occurs sympatric in parts of the distribution area . The male can be distinguished from Z. rufipes on the basis of the large patch of white scales at the beginning of the sloping chest section; it also has a longitudinal split on the bulb of the pedipalp . The females differ in the shape of the epigyne .
distribution and habitat
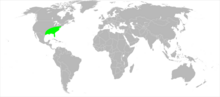
The range of this species stretches from New Jersey to Florida and west to Texas , with it being found most commonly in the southern states. It usually lives in the herb layer of the temperate deciduous forests.
development
The young spiders of Z. sexpunctatus hatch from the egg cocoons in the middle of summer . The spiders hibernate as a juvenile form and usually reach sexual maturity in April to May.
Systematics
The first description of the species was made by the entomologist Nicholas Marcellus Hentz in 1845 as Attus sexpunctatus . In 1888 Zygoballus was described as a genus of its own and George and Elizabeth Peckham classified this species as Zygoballus sexpunctatus . The genus Zygoballus is now assigned to the subfamily Dendryphantinae within the jumping spiders (Salticidae).
Web links
Zygoballus sexpunctatus in the World Spider Catalog
- Zygoballus sexpunctatus in the Nearctic Spider Database
- Zygoballus sexpunctatus on Bugguide.net
- Zygoballus sexpunctatus in Salticidae: Diagnostic Drawings Library
- Behavior of Zygoballus sexpunctatus spiders (video)
- Interactions of male and female Zygoballus sexpunctatus spiders (video)
Individual evidence
- ^ A b c d W. Mike Howell, Ronald L. Jenkins: Spiders of the Eastern United States: A Photographic Guide . Pearson Education, 2004, pp. 339-340.
- ^ A b I. L. Ressler: Spiders of the Family Attidae Collected in the Vicinity of Ames, Iowa . In: Proceedings of the Iowa Academy of Science . 25, 1918, pp. 230-231.
- ^ A b George Peckham, Elizabeth Peckham: Attidae of North America . In: Transactions of the Wisconsin Academy of Sciences, Arts, and Letters . 7, 1888, p. 89.
- ^ Nicholas Hentz: The Spiders of the United States . Boston Society of Natural History, 1875, p. 54.
- ^ A b c d e John Henry Comstock [First published 1912]: The Spider Book . Cornell University Press, 1920, pp. 696-699.
- ^ A b Walter William Gibson: An Ecological Study of the Spiders of a River-Terrace Forest in Western Tennessee . In: Ohio Journal of Science . 47, No. 1, 1947, pp. 38-44.
- ^ Norman I. Platnick: The World Spider Catalog, Version 10.0 . American Museum of Natural History. 2009. Retrieved March 9, 2011.