USS Hulbert: Difference between revisions
changed Palmyra to Palmyra Atoll |
|||
| (29 intermediate revisions by 19 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{short description|Tender of the United States Navy}} |
|||
{|{{Infobox ship begin}} |
{|{{Infobox ship begin}} |
||
{{Infobox ship image |
{{Infobox ship image |
||
|Ship image=[[Image:USS Hulbert (DD-342).jpg|300px|USS Hulbert (DD-342)]] |
|Ship image=[[Image:USS Hulbert (DD-342) underway at sea, circa 1930 (NH 67664).jpg|300px|USS Hulbert (DD-342)]] |
||
|Ship caption= |
|Ship caption= |
||
}} |
}} |
||
{{Infobox ship career |
{{Infobox ship career |
||
|Hide header= |
|Hide header= |
||
|Ship country= |
|Ship country=United States |
||
|Ship flag={{USN flag|1945}} |
|Ship flag={{USN flag|1945}} |
||
|Ship name= |
|Ship name= |
||
| Line 22: | Line 24: | ||
|Ship reinstated= |
|Ship reinstated= |
||
|Ship honours= |
|Ship honours= |
||
|Ship fate= |
|Ship fate=Sold for scrap, 31 October 1946 |
||
|Ship status= |
|||
|Ship notes= |
|Ship notes= |
||
}} |
}} |
||
| Line 31: | Line 32: | ||
|Ship class= [[Clemson class destroyer|''Clemson''-class]] [[destroyer]] |
|Ship class= [[Clemson class destroyer|''Clemson''-class]] [[destroyer]] |
||
|Ship displacement=1,190 tons |
|Ship displacement=1,190 tons |
||
|Ship length=314 |
|Ship length={{convert|314|ft|5|in|m}} |
||
|Ship beam=30 |
|Ship beam={{convert|30|ft|8|in|m}} |
||
|Ship draft=9 |
|Ship draft={{convert|9|ft|3|in|m}} |
||
|Ship propulsion=26,500 shp (20 MW); |
|Ship propulsion=*26,500 shp (20 MW); |
||
*geared turbines, |
|||
*2 screws |
|||
|Ship speed=35 |
|Ship speed={{convert|35|kn|km/h}} |
||
|Ship range=4,900 [[Nautical mile|nmi]] (9,100 km) |
|Ship range=*4,900 [[Nautical mile|nmi]] (9,100 km) |
||
* @ 15 [[knot (unit)|kt]] |
|||
|Ship complement=126 officers and enlisted |
|Ship complement=126 officers and enlisted |
||
|Ship sensors= |
|Ship sensors= |
||
|Ship EW= |
|Ship EW= |
||
|Ship armament=4 × 4" |
|Ship armament=4 × [[4"/50 caliber gun|{{convert|4|in|mm|abbr=on|0}}/50]] guns, 2 × [[3"/23 caliber gun|{{convert|3|in|mm|abbr=on|0}}/25]] guns, 12 × [[American 21 inch torpedo|21 inch (533 mm)]] [[torpedo tube]]s |
||
|Ship armour= |
|Ship armour= |
||
|Ship armor= |
|Ship armor= |
||
| Line 49: | Line 53: | ||
|} |
|} |
||
'''USS ''Hulbert'' (DD-342/AVD-6)''' was a [[Clemson class destroyer|''Clemson''-class]] [[destroyer]] in the [[United States Navy]] following [[World War I]]. She was named for [[Henry Hulbert]]. |
|||
== Service history == |
|||
==History== |
|||
''Hulbert'' was launched by [[Norfolk Navy Yard]], [[Portsmouth, Virginia]], 28 June 1918; sponsored by Mrs. V. C. Hulbert, widow of Lieutenant Hulbert; and commissioned 27 October 1920 |
''Hulbert'' was launched by [[Norfolk Navy Yard]], [[Portsmouth, Virginia]], 28 June 1918; sponsored by Mrs. V. C. Hulbert, widow of Lieutenant Hulbert; and commissioned 27 October 1920. |
||
=== Prewar service === |
|||
Following shakedown training out of [[Norfolk, Virginia]], ''Hulbert'' took part in destroyer maneuvers in the Atlantic until June 1921, when she assisted in ordnance tests on obsolete American and captured [[Germany|German]] ships. For the next year, the ship operated out of [[Newport, Rhode Island|Newport]] with other destroyers. |
Following shakedown training out of [[Norfolk, Virginia]], ''Hulbert'' took part in destroyer maneuvers in the Atlantic until June 1921, when she assisted in ordnance tests on obsolete American and captured [[Germany|German]] ships. For the next year, the ship operated out of [[Newport, Rhode Island|Newport]] with other destroyers. |
||
''Hulbert'' sailed 20 June 1922 for duty on the [[Asiatic Station]], steaming via the [[Mediterranean]] and [[Ceylon]] to [[Chefoo]], [[China]], 26 August. The ship patrolled Chinese and [[Philippines|Philippine]] waters in the year that followed, protecting American interests during the [[Chinese Civil War]]. She also took part in periodic fleet exercises designed to keep her crew and equipment at maximum |
''Hulbert'' sailed 20 June 1922 for duty on the [[Asiatic Station]], steaming via the [[Mediterranean]] and [[Ceylon]] to [[Chefoo]], [[China]], 26 August. The ship patrolled Chinese and [[Philippines|Philippine]] waters in the year that followed, protecting American interests during the [[Chinese Civil War]]. On the night of 28 February 1923, six crew were killed in the engine room when furnace oil flared back and trapped them.<ref>United Press, "Six Killed In Warship Blast", ''The Madera Daily Tribune'', Madera, California, Thursday 1 March 1923, Volume XXXI, Number 98, page 1.</ref> She also took part in periodic fleet exercises designed to keep her crew and equipment at maximum readiness. ''Hulbert'' took part in the evacuation of American civilians and missionaries in March 1927 and September 1928. Completing this lengthy tour of duty in the Far East, she sailed 22 July 1929 from [[Yokohama]], arriving San Diego 17 August. |
||
During the remainder of the year, ''Hulbert'' acted as plane guard for carriers {{USS|Langley|CV-1|2}} and {{USS|Saratoga|CV-3|2}} off [[California]], thus helping to develop carrier-group tactics. She took part in important fleet exercises on both coasts, during the period from 1930 to 1934 and arrived [[Philadelphia |
During the remainder of the year, ''Hulbert'' acted as plane guard for carriers {{USS|Langley|CV-1|2}} and {{USS|Saratoga|CV-3|2}} off [[California]], thus helping to develop carrier-group tactics. She took part in important fleet exercises on both coasts, during the period from 1930 to 1934 and arrived [[Philadelphia]] 14 August 1934. She decommissioned there 17 October 1934 and was placed in reserve. |
||
''Hulbert'' was converted to a [[seaplane tender]], recommissioning at [[New York Navy Yard]] as '''AVD-6''' on 2 August 1940. She arrived in San Diego 24 August via [[Guantánamo Bay, Cuba|Guantanamo Bay]] and the [[Panama Canal Zone]], and began servicing Patrol Wing 1 on operations off the West Coast, helping to perfect America's seaplane reconnaissance capability. ''Hulbert'' sailed 8 May 1941 for Pearl Harbor, where she became headquarters ship for the seaplane wing and continued servicing and repairing her planes. |
''Hulbert'' was converted to a [[seaplane tender]], recommissioning at [[New York Navy Yard]] as '''AVD-6''' on 2 August 1940. She arrived in San Diego 24 August via [[Guantánamo Bay, Cuba|Guantanamo Bay]] and the [[Panama Canal Zone]], and began servicing Patrol Wing 1 on operations off the West Coast, helping to perfect America's seaplane reconnaissance capability. ''Hulbert'' sailed 8 May 1941 for Pearl Harbor, where she became headquarters ship for the seaplane wing and continued servicing and repairing her planes. |
||
==World War II== |
=== World War II and postwar service === |
||
On the morning of 7 December 1941, during the [[attack on Pearl Harbor]], ''Hulbert'' was moored at the Submarine Base, [[Pearl Harbor]]. General Quarters sounded just before 08:00, and the ship's antiaircraft batteries immediately opened fire at attacking planes. This vessel went to general quarters when the Japanese attack was first sighted by the watch aboard, and is believed to have been the first ship in the fleet to open fire. |
On the morning of 7 December 1941, during the [[attack on Pearl Harbor]], ''Hulbert'' was moored at the Submarine Base, [[Pearl Harbor]]. General Quarters sounded just before 08:00, and the ship's antiaircraft batteries immediately opened fire at attacking planes. This vessel went to general quarters when the Japanese attack was first sighted by the watch aboard, and is believed to have been the first ship in the fleet to open fire. As the Japanese directed their attention to [[Ford Island]] and the [[battleship]]s, she shot down one torpedo plane at 0758, shared in bringing down a dive bomber at about 0820 and damaged several other aircraft. After the attack the ship assisted in the rescue effort. After loading ammunition, she moved to Hilo 9 December to set up an advance base for the all-important patrol bombers. ''Hulbert'' was also called upon to aid aircraft at sea, as on Christmas Day she repaired a seaplane at sea and then towed it for nearly 3 days when heavy seas prevented a safe takeoff. |
||
After sundown on 30 December 1941 ''Hulbert'' was engaged by [[Japanese submarine I-1|Japanese submarine ''I-1'']] while moored. The IJN vessel claimed moderate damage and hit the adjacent pier. ''Hulbert'' returned fire, aided by a local Coast Artillery unit.<ref>[http://www.combinedfleet.com/type_j1.htm Submarine Type J-1]</ref><ref name="I-1Tab2">{{cite web|url=http://www.combinedfleet.com/I-1.htm|title=IJN Submarine ''I-1'': Tabular Record of Movement|last1=Hackett|first1=Bob|last2=Kingsepp|first2=Sander|website=CombinedFleet.com|access-date=24 September 2018}}</ref> |
|||
| ⚫ | The Japanese had occupied [[Kiska]] and [[Attu Island|Attu]] as part of the abortive [[Battle of Midway|Midway]] Offensive, and ''Hulbert'' was assigned to tend the seaplanes of VP-43 during reconnaissance flights and bombing raids on those islands. The ship also steamed to Seguam Island 30 August 1942, landing a party of marines to search for a Japanese radio station. Next day, she arrived in Atka to aid torpedoed tender [[USS Casco (AVP-12)| |
||
| ⚫ | The ship also made supply runs to [[Palmyra Atoll]] before moving north to [[Kodiak, Alaska|Kodiak]] 6 June 1942. The Japanese had occupied [[Kiska]] and [[Attu Island|Attu]] as part of the abortive [[Battle of Midway|Midway]] Offensive, and ''Hulbert'' was assigned to tend the seaplanes of VP-43 during reconnaissance flights and bombing raids on those islands. The ship also steamed to Seguam Island 30 August 1942, landing a party of marines to search for a Japanese radio station. Next day, she arrived in Atka to aid torpedoed tender [[USS Casco (AVP-12)|USS ''Casco'']], alternating between salvage efforts and seaplane tending during September. ''Hulbert'' sailed 4 October for supplies and repairs at [[San Francisco, California]]. |
||
[[File:USS Hulbert (AVD-6) stranded on Attu 1943.jpg|thumb|''Hulbert'' stranded on Attu, 1943.]] |
[[File:USS Hulbert (AVD-6) stranded on Attu 1943.jpg|thumb|''Hulbert'' stranded on Attu, 1943.]] |
||
| Line 71: | Line 79: | ||
She was again underway from [[Seattle, Washington]] 8 December 1942 for Kodiak where the ship serviced patrol bombers during the first months of 1943. In May ''Hulbert'' moved to [[Amchitka]], acting as communications ship during the recapture of [[Attu Island|Attu]] that spring. She moved again to Attu in June, to provide fuel and communications services for seaplanes and torpedo boats but was blown ashore in Massacre Bay during a severe storm 30 June 1943. ''Hulbert's'' hull was seriously damaged and, after temporary repairs at [[Dutch Harbor]], she arrived in Seattle 30 August for a major overhaul. |
She was again underway from [[Seattle, Washington]] 8 December 1942 for Kodiak where the ship serviced patrol bombers during the first months of 1943. In May ''Hulbert'' moved to [[Amchitka]], acting as communications ship during the recapture of [[Attu Island|Attu]] that spring. She moved again to Attu in June, to provide fuel and communications services for seaplanes and torpedo boats but was blown ashore in Massacre Bay during a severe storm 30 June 1943. ''Hulbert's'' hull was seriously damaged and, after temporary repairs at [[Dutch Harbor]], she arrived in Seattle 30 August for a major overhaul. |
||
The ship was reclassified DD-342 on 1 December 1943, and sailed 15 January 1944 to San Diego to take up new duties as an escort ship. For the remainder of the war ''Hulbert'' acted as plane guard and screen ship for dozens of new escort carriers as they made ready to join America's striking fleet in the Far East. The ship also served as a maneuvering torpedo target during pilot training and rescued a dozen pilots during this period. After the war's end, ''Hulbert'' sailed 30 September, escorting carrier [[USS Ranger (CV-4)| |
The ship was reclassified DD-342 on 1 December 1943, and sailed 15 January 1944 to San Diego to take up new duties as an escort ship. For the remainder of the war ''Hulbert'' acted as plane guard and screen ship for dozens of new escort carriers as they made ready to join America's striking fleet in the Far East. The ship also served as a maneuvering torpedo target during pilot training and rescued a dozen pilots during this period. After the war's end, ''Hulbert'' sailed 30 September, escorting carrier [[USS Ranger (CV-4)|USS ''Ranger'']] to the [[Panama Canal Zone]] and arrived Philadelphia 17 October 1945. |
||
| ⚫ | |||
==Fate== |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
''Hulbert'' received two battle stars for World War II service. |
''Hulbert'' received two battle stars for World War II service. |
||
| Line 81: | Line 88: | ||
==References== |
==References== |
||
{{reflist}} |
|||
*{{DANFS|http://www.history.navy.mil/danfs/ |
*{{DANFS|http://www.history.navy.mil/research/histories/ship-histories/danfs/h/hulbert.html}} |
||
==External links== |
==External links== |
||
| Line 88: | Line 96: | ||
{{Clemson class destroyer}} |
{{Clemson class destroyer}} |
||
{{June 1943 shipwrecks}} |
|||
{{Use dmy dates|date= |
{{Use dmy dates|date=July 2019}} |
||
{{DEFAULTSORT:Hulbert (Dd-342)}} |
{{DEFAULTSORT:Hulbert (Dd-342)}} |
||
| Line 99: | Line 107: | ||
[[Category:Ships present during the attack on Pearl Harbor]] |
[[Category:Ships present during the attack on Pearl Harbor]] |
||
[[Category:Ships built in Portsmouth, Virginia]] |
[[Category:Ships built in Portsmouth, Virginia]] |
||
[[Category:Maritime incidents in June 1943]] |
|||
Latest revision as of 10:11, 6 January 2024
| |
| History | |
|---|---|
| Namesake | Henry Hulbert |
| Builder | Norfolk Naval Shipyard |
| Laid down | 18 November 1918 |
| Launched | 28 June 1919 |
| Commissioned | 27 October 1920 |
| Decommissioned | 2 November 1945 |
| Stricken | 28 November 1945 |
| Fate | Sold for scrap, 31 October 1946 |
| General characteristics | |
| Class and type | Clemson-class destroyer |
| Displacement | 1,190 tons |
| Length | 314 feet 5 inches (95.83 m) |
| Beam | 30 feet 8 inches (9.35 m) |
| Draft | 9 feet 3 inches (2.82 m) |
| Propulsion |
|
| Speed | 35 knots (65 km/h) |
| Range | |
| Complement | 126 officers and enlisted |
| Armament | 4 × 4 in (102 mm)/50 guns, 2 × 3 in (76 mm)/25 guns, 12 × 21 inch (533 mm) torpedo tubes |
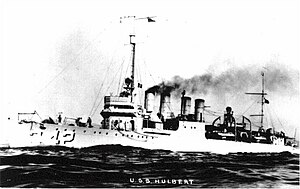
USS Hulbert (DD-342/AVD-6) was a Clemson-class destroyer in the United States Navy following World War I. She was named for Henry Hulbert.
Service history[edit]
Hulbert was launched by Norfolk Navy Yard, Portsmouth, Virginia, 28 June 1918; sponsored by Mrs. V. C. Hulbert, widow of Lieutenant Hulbert; and commissioned 27 October 1920.
Prewar service[edit]
Following shakedown training out of Norfolk, Virginia, Hulbert took part in destroyer maneuvers in the Atlantic until June 1921, when she assisted in ordnance tests on obsolete American and captured German ships. For the next year, the ship operated out of Newport with other destroyers.
Hulbert sailed 20 June 1922 for duty on the Asiatic Station, steaming via the Mediterranean and Ceylon to Chefoo, China, 26 August. The ship patrolled Chinese and Philippine waters in the year that followed, protecting American interests during the Chinese Civil War. On the night of 28 February 1923, six crew were killed in the engine room when furnace oil flared back and trapped them.[1] She also took part in periodic fleet exercises designed to keep her crew and equipment at maximum readiness. Hulbert took part in the evacuation of American civilians and missionaries in March 1927 and September 1928. Completing this lengthy tour of duty in the Far East, she sailed 22 July 1929 from Yokohama, arriving San Diego 17 August.
During the remainder of the year, Hulbert acted as plane guard for carriers Langley and Saratoga off California, thus helping to develop carrier-group tactics. She took part in important fleet exercises on both coasts, during the period from 1930 to 1934 and arrived Philadelphia 14 August 1934. She decommissioned there 17 October 1934 and was placed in reserve.
Hulbert was converted to a seaplane tender, recommissioning at New York Navy Yard as AVD-6 on 2 August 1940. She arrived in San Diego 24 August via Guantanamo Bay and the Panama Canal Zone, and began servicing Patrol Wing 1 on operations off the West Coast, helping to perfect America's seaplane reconnaissance capability. Hulbert sailed 8 May 1941 for Pearl Harbor, where she became headquarters ship for the seaplane wing and continued servicing and repairing her planes.
World War II and postwar service[edit]
On the morning of 7 December 1941, during the attack on Pearl Harbor, Hulbert was moored at the Submarine Base, Pearl Harbor. General Quarters sounded just before 08:00, and the ship's antiaircraft batteries immediately opened fire at attacking planes. This vessel went to general quarters when the Japanese attack was first sighted by the watch aboard, and is believed to have been the first ship in the fleet to open fire. As the Japanese directed their attention to Ford Island and the battleships, she shot down one torpedo plane at 0758, shared in bringing down a dive bomber at about 0820 and damaged several other aircraft. After the attack the ship assisted in the rescue effort. After loading ammunition, she moved to Hilo 9 December to set up an advance base for the all-important patrol bombers. Hulbert was also called upon to aid aircraft at sea, as on Christmas Day she repaired a seaplane at sea and then towed it for nearly 3 days when heavy seas prevented a safe takeoff.
After sundown on 30 December 1941 Hulbert was engaged by Japanese submarine I-1 while moored. The IJN vessel claimed moderate damage and hit the adjacent pier. Hulbert returned fire, aided by a local Coast Artillery unit.[2][3]
The ship also made supply runs to Palmyra Atoll before moving north to Kodiak 6 June 1942. The Japanese had occupied Kiska and Attu as part of the abortive Midway Offensive, and Hulbert was assigned to tend the seaplanes of VP-43 during reconnaissance flights and bombing raids on those islands. The ship also steamed to Seguam Island 30 August 1942, landing a party of marines to search for a Japanese radio station. Next day, she arrived in Atka to aid torpedoed tender USS Casco, alternating between salvage efforts and seaplane tending during September. Hulbert sailed 4 October for supplies and repairs at San Francisco, California.

She was again underway from Seattle, Washington 8 December 1942 for Kodiak where the ship serviced patrol bombers during the first months of 1943. In May Hulbert moved to Amchitka, acting as communications ship during the recapture of Attu that spring. She moved again to Attu in June, to provide fuel and communications services for seaplanes and torpedo boats but was blown ashore in Massacre Bay during a severe storm 30 June 1943. Hulbert's hull was seriously damaged and, after temporary repairs at Dutch Harbor, she arrived in Seattle 30 August for a major overhaul.
The ship was reclassified DD-342 on 1 December 1943, and sailed 15 January 1944 to San Diego to take up new duties as an escort ship. For the remainder of the war Hulbert acted as plane guard and screen ship for dozens of new escort carriers as they made ready to join America's striking fleet in the Far East. The ship also served as a maneuvering torpedo target during pilot training and rescued a dozen pilots during this period. After the war's end, Hulbert sailed 30 September, escorting carrier USS Ranger to the Panama Canal Zone and arrived Philadelphia 17 October 1945.
She decommissioned 2 November 1945 and was sold for scrap on 31 October 1946 to Ship Shape, Inc., Philadelphia.
Hulbert received two battle stars for World War II service.
As of 2009, no other ship has been named USS Hulbert.
References[edit]
- ^ United Press, "Six Killed In Warship Blast", The Madera Daily Tribune, Madera, California, Thursday 1 March 1923, Volume XXXI, Number 98, page 1.
- ^ Submarine Type J-1
- ^ Hackett, Bob; Kingsepp, Sander. "IJN Submarine I-1: Tabular Record of Movement". CombinedFleet.com. Retrieved 24 September 2018.
 This article incorporates text from the public domain Dictionary of American Naval Fighting Ships. The entry can be found here.
This article incorporates text from the public domain Dictionary of American Naval Fighting Ships. The entry can be found here.
External links[edit]
