β-mannosidosis
| Classification according to ICD-10 | |
|---|---|
| E77.1 | Defects in glycoprotein degradation mannosidosis |
| ICD-10 online (WHO version 2019) | |
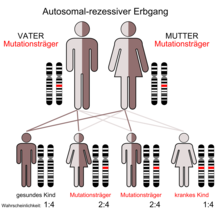
The β-Mannosidosis is an extremely rare autosomal - recessive inherited lysosomal storage disease from the group of oligosaccharidoses .
Prevalence
With a prevalence of less than 1: 1,000,000 in live-born children, β-mannosidosis is an extremely rare disease. Globally, only 20 cases in 16 families were reported by 2008. Due to the poor data situation, the symptoms are not described with sufficient certainty.
Symptoms
Similar to α-mannosidosis , β-mannosidosis in the affected patients is characterized by immune weakness , mental retardation, delayed speech development, changes in the skeleton and hearing loss . In addition, there are hypotension and seizures in some cases . The weakened immune system results in recurrent respiratory infections .
Genetics and Pathogenesis
Β-mannosidosis is based on an autosomal recessive inheritance . Mutations in manba - gene , located on chromosome 4 gene locus is q22-q25, are the cause of the disease. The MANBA gene codes for the enzyme β-mannosidase . Mutations in this gene product can cause a reduced activity of β-mannosidase, as a result of which disaccharides from mannose accumulate in the tissue of the affected patient .
diagnosis
The diagnosis can be made by determining the activity of β-mannosidase in leukocytes or cultured fibroblasts. A DNA analysis ('genetic test') can be performed to confirm the results. Excretion of increased amounts of mannose disaccharide in the urine is an indication of the disease, but not specific evidence. A prenatal diagnosis is possible both biochemically and molecularly genetically.
therapy
A specific therapy is not yet known. The disease is treated purely symptomatically.
Initial description and veterinary medicine
The disease was first described in goats in 1981 and five years later in humans. The disease progression in goats is much more serious and leads to an early death of the animals. The disease was first diagnosed in cattle in 1993.
further reading
- M. Zhu et al. a .: Beta-mannosidosis mice: a model for the human lysosomal storage disease. In: Hum Molec Genet 15, 2006, pp. 493-500, PMID 16377659 .
- JR Leipprandt u. a .: Caprine beta-mannosidase: sequencing and characterization of the cDNA and identification of the molecular defect of caprine beta-mannosidosis. IN: Genomics 37, 1996, pp. 51-56, PMID 8921369 .
- T. Levade et al. a .: Human beta-mannosidase deficiency associated with peripheral neuropathy. In: Ann Neurol 35, 1994, pp. 116-119, PMID 8285582 .
- JA Malachowski and MZ Jones: Beta-mannosidosis: lesions of the distal peripheral nervous system. In: Acta Neuropath 61, 1983, pp. 95-100, PMID 6637401 .
- KL Lovell and MZ Jones: Distribution of central nervous system lesions in beta-mannosidosis. In: Acta Neuropath 62, 1983, pp. 121-126, PMID 6659869 .
Web links
- Β-mannosidosis. In: Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man . (English)
- Β-mannosidosis. In: Orphanet (Rare Disease Database).
Individual evidence
- ↑ HMF Riise Stensland u. a .: Identification of two novel beta-mannosidosis-associated sequence variants: biochemical analysis of beta-mannosidase (MANBA) missense mutations. In: Molec Genet Metab 94, 2008, pp. 476-480, PMID 18565776 .
- ↑ a b c Β-mannosidosis. In: Orphanet (Rare Disease Database).
- ↑ a b M.Z. Jones and G. Dawson: Caprine beta-mannosidosis: inherited deficiency of beta-D-mannosidase. In: J Biol Chem 256, 1981, pp. 5185-5188, PMID 7228876 .
- ↑ DA Wenger u. a .: Human beta-mannosidase deficiency. In: NEJM 315, 1986, pp. 1201-1205, PMID 2945113 .
- ↑ MZ Jones and B. Abbitt: Animal model of human disease: bovine beta-mannosidosis. In: Am J Path 142, 1993, pp. 957-960, PMID 8456950 .