Iodophenols
| Iodophenols | |||||||
| Surname | 2-iodophenol | 3-iodophenol | 4-iodophenol | ||||
| other names | o -iodophenol | m -iodophenol | p -iodophenol | ||||
| Structural formula |
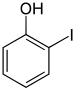
|

|

|
||||
| CAS number | 533-58-4 | 626-02-8 | 540-38-5 | ||||
| PubChem | 10784 | 12272 | 10894 | ||||
| Molecular formula | C 6 H 5 IO | ||||||
| Molar mass | 220.01 g mol −1 | ||||||
| Physical state | firmly | ||||||
| Melting point | 43 ° C | 40 ° C | 92-94 ° C | ||||
| boiling point | 186-187 ° C (160 torr ) |
||||||
| pK s value | 8.46 | 9.17 | 9.20 | ||||
|
GHS labeling |
|
|
|
||||
| H and P phrases | 302-312-315-319-332-335 | 315-319-335 | 302-312-314 | ||||
| no EUH phrases | no EUH phrases | no EUH phrases | |||||
| 261-280-305 + 351 + 338 | 261-305 + 351 + 338 | 280-305 + 351 + 338-310 | |||||
The iodophenols form a group of substances in chemistry that is derived from both phenol and iodobenzene . The structure consists of a benzene ring with attached hydroxyl group (-OH) and iodine (-I) as substituents . Their different arrangement results in three constitutional isomers with the empirical formula C 6 H 5 IO.
properties
The 4-iodophenol, which has the highest symmetry, has the highest melting point. The iodophenols have a higher acidity than phenol due to the −I effect of the iodine substituent. The pK s values are therefore correspondingly lower (phenol: 9.99).
presentation
The iodophenols can be prepared from the iodanilines by boiling their diazonium salts .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f CRC Handbook of Tables for Organic Compound Identification , Third Edition, 1984, ISBN 0-8493-0303-6 .
- ↑ 2-Iodophenol data sheet from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on May 3, 2011 ( PDF ).
- ↑ Data sheet 3-Iodophenol from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on May 3, 2011 ( PDF ).
- ↑ Data sheet 4-iodophenol from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on May 3, 2011 ( PDF ).

