Chlorophenols
| Chlorophenols | |||||
| Surname | 2-chlorophenol | 3-chlorophenol | 4-chlorophenol | ||
| other names | 2-CP o -chlorophenol 1-chloro-2-hydroxybenzene 1-oxy-2-chlorobenzene |
3-CP m -chlorophenol 1-chloro-3-hydroxybenzene 1-oxy-3-chlorobenzene |
4-CP p -chlorophenol 1-chloro-4-hydroxybenzene 1-oxy-4-chlorobenzene |
||
| Structural formula |

|

|
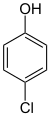
|
||
| CAS number | 95-57-8 | 108-43-0 | 106-48-9 | ||
| 25167-80-0 (mixture of isomers) | |||||
| PubChem | 7245 | 7933 | 4684 | ||
| Molecular formula | C 6 H 5 ClO | ||||
| Molar mass | 128.56 g mol −1 | ||||
| Physical state | liquid | firmly | |||
| Brief description | colorless liquid with a pungent odor |
colorless crystal needles with a phenol-like odor |
|||
| Melting point | 7 ° C | 33-35 ° C | 43 ° C | ||
| boiling point | 174 ° C | 214 ° C | 220 ° C | ||
| density | 1.26 g cm −3 | 1.25 g cm −3 | 1.31 g cm −3 | ||
| Vapor pressure | 2.3 mbar (20 ° C) | 0.23 mbar (20 ° C) | 0.15 mbar (20 ° C) | ||
| pK s value | 8.48 | 9.08 | 9.38 | ||
| solubility | slightly soluble in water (27–29 g / l at 20 ° C) | ||||
| Flash point | 85 ° C | 120 ° C | 121 ° C | ||
|
GHS labeling |
|
||||
| H and P phrases | 302-312-332-411 | ||||
| no EUH phrases | |||||
| 273 | 273-280 | 273-302 + 352 | |||
| Toxicological data | 40 mg kg −1 ( LD 50 , rat , oral ) | 570 mg kg −1 ( LD 50 , rat , oral ) | 670 mg kg −1 ( LD 50 , rat , oral ) | ||
In chemistry , the chlorophenols form a group of substances that are derived from both phenol and chlorobenzene . The structure consists of a benzene ring with attached hydroxyl group (-OH) and chlorine (-Cl) as substituents . Their different arrangement results in three constitutional isomers with the empirical formula C 6 H 5 ClO.
properties
Chlorophenols are poorly water-soluble, non-volatile, toxic, sometimes carcinogenic compounds that are often used as wood preservatives , herbicides and fungicides , for bleaching cellulose in paper production and as intermediates in the synthesis of drugs and dyes. Since they are chemically very stable, they accumulate in the food chain . When chlorophenols are heated, polychlorinated dibenzodioxins can be formed with the elimination of hydrogen chloride .
The 4-chlorophenol, which has the highest symmetry, has the highest melting point. The chlorophenols have a higher acidity compared to phenol due to the −I effect of the chlorine substituent. The pK s values are therefore correspondingly lower (phenol: 9.99).
use
2-chlorophenol is used in the manufacture of drugs and dyes as well as a disinfectant and appears as a pollutant in groundwater. 3-chlorophenol and 4-chlorophenol are used as intermediate products in the manufacture of pharmaceuticals and dyes and as disinfectants.
More connections
The expanded group of chlorophenols (CP) includes a total of 19 chemical compounds that can be produced in phenol by substituting chlorine for the hydrogen atoms .
Depending on the number of chlorine atoms, one differentiates:
- Monochlorophenols (2-CP, 3-CP, 4-CP)
- Dichlorophenols (2,3-DCP, 2,4-DCP , 2,5-DCP, 2,6-DCP, 3,4-DCP, 3,5-DCP)
- Trichlorophenols (2,3,4-TCP, 2,3,5-TCP, 2,3,6-TCP, 2,4,5-TCP , 2,4,6-TCP , 3,4,5-TCP)
- Tetrachlorophenols (2,3,4,5-TeCP, 2,3,4,6-TeCP, 2,3,5,6-TeCP)
- Pentachlorophenol (PCP)
With the exception of 2-chlorophenol , all compounds of the group are solid at room temperature.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g h Entry on 2-chlorophenol in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on October 14, 2012(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ a b c d e f g h Entry on 3-chlorophenol in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on October 14, 2012(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ a b c d e f g h Entry on 4-chlorophenol in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on October 14, 2012(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ a b CRC Handbook of Tables for Organic Compound Identification , Third Edition, 1984, ISBN 0-8493-0303-6 .
Web links
- Chlorophenols
- "Remove environmental toxins in a gentle way" , Berliner Zeitung , April 12, 2002.
- Substance monograph chlorophenols - reference values. Statement by the “Human Biomonitoring” commission of the Federal Environment Agency (PDF; 1.1 MB) In: Federal Health Gazette - Health Research - Health Protection . 52, 2009, pp. 987-1002, doi : 10.1007 / s00103-009-0947-9

