AP-1
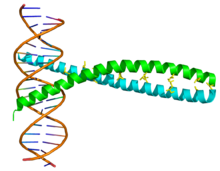
AP-1 is a transcription factor . AP-1 is a heterodimeric protein complex made up of proteins from the ATF , JDP , c-Fos and c-Jun families and binds as a dimer to DNA in order to initiate the transcription of certain genes .
properties
The genes regulated by AP-1 include genes for cell differentiation , cell division, and apoptosis . The gene expression of AP-1 itself is induced by cytokines , growth factors , infections and stress factors . AP-1 binds to DNA via basic amino acids , while dimerization is mediated by a leucine zipper . AP-1 enhances gene expression on the 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate DNA response element ( TRE , sequence 5'-TGAG / CTCA-3 ').
Individual evidence
- ↑ Ameyar M, Wisniewska M, Weitzman JB: A role for AP-1 in apoptosis: the case for and against . In: Biochemistry . 85, No. 8, August 2003, pp. 747-52. doi : 10.1016 / j.biochi.2003.09.006 . PMID 14585541 .
- ↑ a b Hess J, Angel P, Schorpp-Kistner M: AP-1 subunits: quarrel and harmony among siblings . In: J. Cell. Sci. . 117, No. Pt 25, 2004, pp. 5965-73. doi : 10.1242 / jcs.01589 . PMID 15564374 .
- ↑ Glover JN, Harrison SC: Crystal structure of the heterodimeric bZIP transcription factor c-Fos-c-Jun bound to DNA . In: Nature . 373, No. 6511, 1995, pp. 257-61. doi : 10.1038 / 373257a0 . PMID 7816143 .