Dimerization
The dimerization (synonym dimerization ) is the assembly of two units ( called monomers ), the product is called dimer .
If three or more molecules or atoms join together, one speaks of trimerization or tetramerization (with four monomers). In this case , the resulting molecules are called trimers , tetramers , etc. Dimerization is a special form of polymerization .
chemistry
In chemistry, dimerization describes the assembly of two identical units:
- A + A → A 2
These can be atoms or molecules . An example is the photocatalyzed dimerization of anthracene :
In polymerizations , dimerization can also occur as a side reaction :
- Nitric oxide (NO) can dimerize to N 2 O 2 in the liquid or solid state .
- The brown nitrogen dioxide (NO 2 ) dimerizes under increased pressure to form colorless dinitrogen tetroxide (N 2 O 4 ).
- Two bromine radicals dimerize to form molecular bromine (Br 2 )
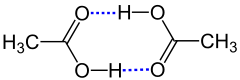
It is also referred to as dimerization when the dimer is only held together by hydrogen bonds , as in the dimerization of carboxylic acids , e.g. B. Acetic acid:
Not only molecules but also radicals can dimerize:
- CH 3 • + CH 3 • → H 3 C-CH 3
Although the molecular formula of a dimer should, strictly speaking, be the doubling of the monomer molecular formula, compounds that are formed by the condensation of two monomers are also called dimers in a broader sense:
- Maltose is a homodimer made from two glucose molecules.
- Cane sugar ( sucrose ) is a heterodimer made from a glucose and a fructose molecule.
- Glycylglycine is the homodimer that results from two glycine molecules through peptide linkage .
In the last three examples mentioned, the sum formula of the dimer is reduced by two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom compared to the sum of the sum formulas of the monomers. In these dimerizations, water (H 2 O) is formed as a by-product.
biochemistry
In the dimerization of biomolecules , a homodimer is created when two monomers of the same type combine (homodimerization) or a heterodimer when two different monomers are involved (heterodimerization). The forces acting in the dimerization of proteins are based predominantly on non- covalent interactions, such as van der Waals forces and hydrogen bonds , electrostatic interactions and hydrophobic effects of the amino acid residues of protein domains close to the surface between the proteins involved . For example, the constituents of an antibody , a light chain and a heavy chain, dimerize . This heterodimer then combines ( dimerizes ) in turn with a second, identically composed heterodimer to form the final antibody.
In chemically induced dimerization , various low molecular weight compounds are used to initiate dimerization of certain fusion proteins .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b entry on dimerization . In: IUPAC Compendium of Chemical Terminology (the “Gold Book”) . doi : 10.1351 / goldbook.D01744 Version: 2.3.3.
- ^ Brockhaus ABC Chemie , VEB FA Brockhaus Verlag Leipzig 1965, p. 299.