Maltose
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
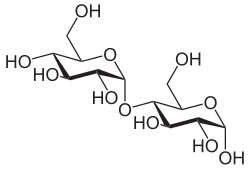
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structural formula of α-maltose | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Maltose | |||||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 12 H 22 O 11 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
white, odorless, sweet-tasting, needle-shaped crystals |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 342.30 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Maltose or malt sugar is a breakdown product of starch . It is a white, crystalline double sugar (disaccharide) with the empirical formula C 12 H 22 O 11 . It dissolves well in water and has a sweetish taste. Based on sucrose , a 10% D -maltose solution has a sweetening power of 41%. The monohydrate is formed when it crystallizes out from aqueous solutions . Maltose comes u. a. in barley sprouts and in potato sprouts.
Maltose should not be confused with maltulose .
Occurrence
Maltose is an ingredient in malt .
Maltose is produced during malting , i.e. the germination of grain, such as B. Barley . Maltose is found in beer , cereals, pasta , potatoes and in many other sweet-tasting products, in which it is formed when starch and glycogen are broken down with α-amylase . Maltose is formed u. a. when brewing beer through the action of amylases on starch in yields of ~ 80%.
Chemical properties
The chemical name for maltose is α - D -glucopyranosyl- (1 → 4) - D -glucopyranose, i.e. H. two D - glucose - molecules are linked to one another acetal-like via a glycosidic and an alcoholic OH group (condensation reaction) (1 → 4- α - glycosidic bond ).
Maltose is in equilibrium between cyclic and open form.
The (1 → 6) -linked compound, α - D -glucopyranosyl- (1 → 6) - D -glucopyranose, is known for short as isomaltose .
use
As an alternative to sucrose , maltose is used in various nutrient media in cell and tissue culture .
Detection reactions
Maltose can be detected semi-quantitatively in an aqueous solution at 70 ° C with ammonia solution ( Wöhlk reaction ) or methylammonium chloride solution ( Fearon 's test) through the formation of a red color.
safety instructions
Maltose is toxic in extremely high doses (LD 50 > 44 g · kg −1 in the mouse, 34.8 g · kg −1 in the rat). Diarrhea occurs at lower doses .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e data sheet maltose (PDF) from Merck , accessed on January 19, 2011.
- ↑ Entry on maltose. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on November 10, 2014.
- ^ A b J. Buckingham: Dictionary of Natural Products. CRC Press, 1994, ISBN 0-412-46620-1 , p. 3758.
- ↑ a b Entry on maltose in the ChemIDplus database of the United States National Library of Medicine (NLM) .
- ↑ a b Drugs in Japan. 1990, p. 1139.
- ↑ a b Yakuri to Chiryo. In: Pharmacology and Therapeutics. Vol. 7, 1979, p. 53.
- ^ Hans-Dieter Belitz, Werner Grosch, Peter Schieberle: Textbook of food chemistry. 6th, completely revised edition. Springer, Berlin 2008, ISBN 978-3-540-73201-3 , p. 263.
- ↑ Eckehard Buddecke: Outline of Biochemistry. 6th edition. Walter de Gruyter Verlag, 1980, ISBN 3-11-008388-4 , p. 165.
- ↑ SRL Fuentes, MBP Calheiros et al .: The effects of silver nitrate and different carbohydrate sources on somatic embryogenesis in Coffea canephora. In: Plant Cell Tissue and Organ Culture. 60 (1) 2000, pp. 5-13.
- ↑ M. Nageli, JE Schmid et al .: Improved formation of regenerable callus in isolated microspore culture of maize: impact of carbohydrates, plating density and time of transfer. In: Plant Cell Reports. 19 (2) 1999, pp. 177-184.
- ↑ Klaus Ruppersberg: Starch digestion by saliva - what does that actually result? A simple maltose detection at the end of the enzymatic hydrolysis of amylose and the surprising presence of glucose in a ratio of 1:15 . In: MNU Journal . tape 69 , no. 5 , 2016, ISSN 0025-5866 ( pedocs.de [accessed on May 3, 2018]).

