Junction box (telephone)
Junction box ( ADo ) is the name for several connector systems of the German Federal Post Office for telephone connections with an ab interface . They were used by the Federal Post Office when the subscriber wanted to operate his phone in different rooms or wanted to connect a private additional device (ZPr) to his connection line . One then speaks of a junction box system (ADoAnl). The TAE system was introduced in 1987 and replaced the ADo system as well as the VDo system.
Junction box system
In principle, a second alarm clock (W2) had to be installed in a junction box system for telephones in which no telephone was permanently connected to the connection line, which signaled incoming calls even when the telephone was not plugged in and which enabled measurements from the central test facility.
ADo ZB 50
When introduced in the 1930s outlets conditioning example 50 ( Z entral b atterie 50 ) including a four-pole were rolling plug (ADoS example 27) and a five pole socket "ADo example, 50" (old designation W 34) were used. The "ADo ZB 50" is available as a surface-mounted and flush-mounted box, in black or ivory.
Contact assignment ADo ZB 50 (W 34)
| connection | Assignment | use |
|---|---|---|
| a | Head of La | Subscriber line feed |
| b | Line Lb | Line subscriber line |
| W2 | Alarm clock w | Line for additional alarm clock |
| c | Earth E. | Signal line ( earth button ) |
| a1 | Head a | switched line a for second socket |
Pin assignment roller plug - ADoS ZB 27
| connection | Assignment | use |
|---|---|---|
| a | Head of La | Subscriber line feed |
| b | Line Lb | Line subscriber line |
| W2 | Alarm clock w | Line for additional alarm clock |
| c | Earth E. | Signal line ( earth button ) |
ADo 4 and ADo 8
The junction box system 94 was introduced by the Deutsche Bundespost as the successor to the ZB 50 . Connection socket 94 (ADo 945) and the connector ADoS 945 were developed for this purpose. The “ADo 945” is available as a four- and eight-pole surface-mounted and flush-mounted box. These two junction boxes were later referred to as "ADo 4" and "ADo 8".
These junction boxes were installed by the Federal Post Office from around 1963 until the introduction of the TAE socket in 1987, whereby the four-pin junction boxes were mainly used for standard telephones. The eight-pole version was used for additional private equipment such as answering machines , automatic dialing devices , modems or later also analog fax machines , but also for telephones with A2 connection .
The connection cords of the end devices were equipped with a corresponding socket connector ( ADoS ). All opening options for junction boxes and devices connected to them were sealed with seals at the time of the Deutsche Bundespost in order to be able to detect unauthorized opening and thus manipulation attempts.
ADo 8 open, with seals
Contact assignment
| Contact | ADo 4 | ADo 8 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | a-core | a-core |
| 2 | unoccupied | earth |
| 3 | b-core | G-core (external charge indicator ) |
| 4th | unoccupied | b-core |
| 5 | earth | b2 wire |
| 6th | unoccupied | Z-wire |
| 7th | W-wire (external alarm clock) | W-wire (external alarm clock) |
| 8th | unoccupied | a2 wire |
Key position
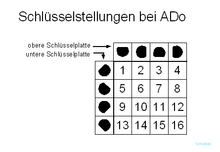
The lid of the ADo has two openings in the middle, behind each of which there is a so-called key plate. This has a circular hole with a flat. The key plates on ADo 4 are installed with the flats facing upwards and cannot be changed. With ADo 8, they can each be inserted rotated in 90 ° steps. This means that 16 different key positions can be set. On the ADo plug there are two key pins as a counterpart , which are inserted in such a way that their flats match the key plates of the junction box provided. This can prevent the wrong insertion of the ADo connector and the insertion of wrong (not intended) end devices. There are also ADo-8 connectors that can be rotated by 45 °, which were also used by the Deutsche Bundespost.
The use of the key positions was specified by the Deutsche Bundespost :
- Key position 1 for telephones that are connected to an ADo 8 instead of an ADo 4.
- Key position 2 for private additional equipment of group A (ZPrA).
- Key position 3 for private additional equipment of group B (ZPrB).
- The key positions 4 to 16 were assigned for additional devices by the Central Telecommunications Office (FTZ):
| Key position | Use case |
|---|---|
| 1 | Intercom (for can system) |
| 2 | Telephone number transmitter , AWAG , connection device for audio reporting, biophonic transmitter, call distributor |
| 3 | Automatic answering machine, speakerphone, biophonic receiver |
| 4th | Facsimile machine, scribe |
| 5 | Malfunction indicator, measured value announcement device |
| 6th | Remote announcement, remote control, remote measurement |
| 7th | Automatic information provider |
| 8th | Telecontrol, telemetry (digital) |
| 9 | Telephone number transmitter with speakerphone |
| 10 | Fax , warning devices |
| 11 | Emergency alarms, private cordless phones and Multitel |
| 12 | Image sending devices |
| 13 | Complaint stations with automatic answering machines |
| 14th | Private playback devices for connections with multiple access |
| 15th | Line telephone according to equipment II |
| 16 | Hazard alarm system in front of the private branch exchange |
The key pins were already supplied by the manufacturers with the key position approved by the FTZ.
ADo 16
Around 1982 the Deutsche Bundespost introduced the 16-pin connection socket “ADo 16” for special devices , telephone desk apparatus with additional device A3, later it was called “TAE 16” socket. The "ADo 16" was also used for other private branch exchanges .
The counterpart to the "ADo 16" is a 16-pin plug with a safety lever (ADoS 16), which was called the "TAE 16" plug from around 1988.
The special devices of the so-called "convenient telephone system" (A3 connection / additional device A3) have integrated electronics that enable up to four telephones to be operated on one exchange line. This telephone system requires an external power supply, the cable of which is either connected to the main telephone or to the "ADo 16" socket. Both have a 5-pin plug connection (ASN) for this purpose.
The first devices of the "telephone-comfort-system" were the " FeTAp 85 " with keypad and the "FeTAp 89" with number switch , followed in 1987 by the "FeTAp 96" with number switch and the "FeTAp 97 / 97a" with keypad. The so-called "convenient telephone system" is a special form of a can system, for example one or more ADo 16, ADo 8 and VDo 4 and VDo 7 were used to build it up.
Contact assignment ADo 16
| connection | Assignment | use |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Power supply unit N5 | Not used, 10 volts ~ |
| 2 | Control core G | Control line from the intent fee display |
| 3 | Line Lb | Subscriber line feed |
| 4th | Head of La | Subscriber line feed |
| 5 | Alarm clock Wa | Second alarm clock for call station 1 |
| 6th | Alarm clock wb | Second alarm clock for call station 1 |
| 7th | Line a2 | Connection for microphone unit 2 |
| 8th | Line b2 | Connection for microphone unit 2 |
| 9 | Line a3 | Connection for intercom 3 |
| 10 | Line b3 | Connection for intercom 3 |
| 11 | Line a4 | Connection for microphone unit 4 |
| 12 | Line b4 | Connection for microphone unit 4 |
| 13 | Power supply unit N4 | Not used (10 volts ~) |
| 14th | Power supply unit N1 | for display of intent charges (35 volts ~) |
| 15th | Power supply unit N2 | Not used, 35 volts ~ |
| 16 | Power pack N3 | Not used, 10 volts ~ |
See also
- Junction box - the corresponding fixed system
- Telephone socket / plug
Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ Handbook of Telecommunications Technology , Volume C7, Call Station Construction. As of summer 1970, p. 52
- ↑ Karl-Heinz Schmidt (Ed.): Terminals on the analog telecommunications network . Rev Deckers's Verlag, G.Schenk, ISBN 3-7685-4889-9 , p. 78